Fig. 7.
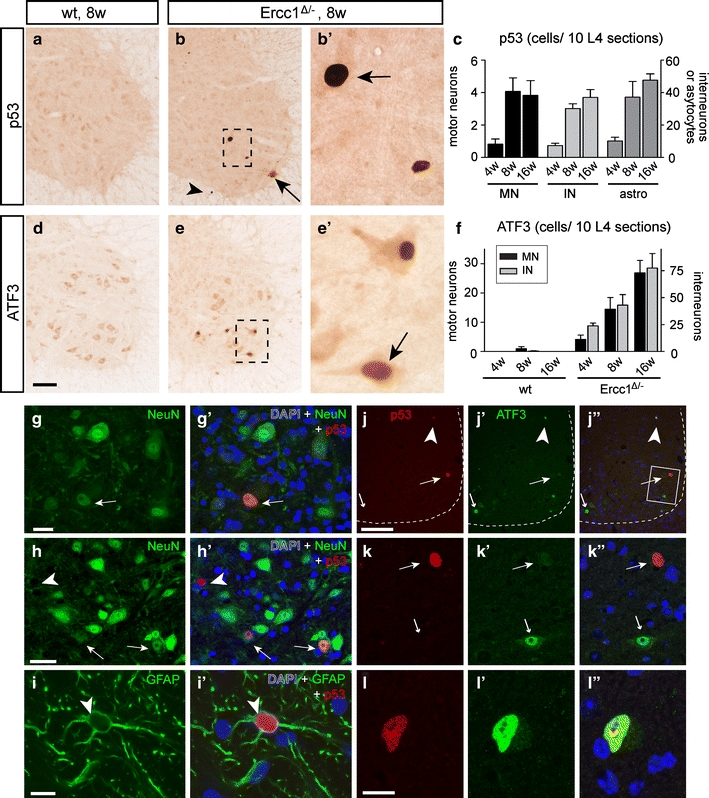
Genotoxic stress-responsive transcription factor p53 and ATF3 expression in Ercc1 Δ/− spinal cord. a–f Photomicrographs (a, b, d, e) and bar graphs (c, f) of p53 (a–c) and ATF3 (d–f) immunostaining, illustrating induction of p53 (arrows; b, b′) and ATF3 (arrow, e′) expression in Ercc1 Δ/− motor neurons. Prominent p53 labeling also occurred in astrocytes (arrowhead, b), while both p53 and ATF3 were expressed by interneurons in the spinal cord intermediate zone and dorsal horn (c, f). Values in c and f are mean ± SE of four mice, while value per mouse is from ten L4 sections. g–i Double-labeling confocal images showing p53–NeuN (g, h) and p53–GFAP (i) double-labeled cells in Ercc1 Δ/− spinal cord. j–l Double-labeling confocal immunofluorescence of p53 and ATF3 showing that p53 and ATF3 in most instances are expressed in distinct cells in Ercc1 Δ/− spinal cord sections. ATF3 single-labeled motor neurons (small arrows; j, k) occurred more frequently than p53 single-labeled motor neurons (large arrows; j, k) and double-labeled cells (arrowhead; j, l). Scale bars 100 μm (d, j), 25 μm (g, h) and 10 μm (i, l)
