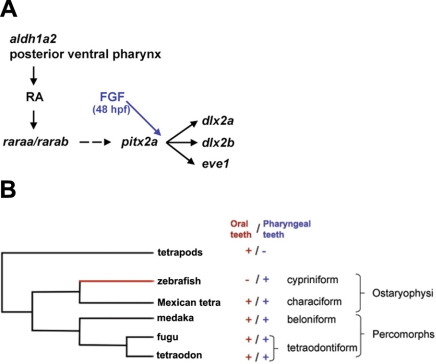
Figure 6.
Proposed model of genetic pathways involved in pharyngeal tooth induction in zebrafish. A) aldh1a2 from the posterior ventral pharynx generates RA. This signal activates the RAR subtype α. RA signaling is required for a proper expression of pitx2a; however, in absence of this signal, pitx2a is still detected at a lower level as a spot at the midline. Dotted lines represent an RA requirement for proper expression of pitx2a. pitx2a, in turn, regulates the expression of dlx2a, dlx2b, and eve1. FGF signaling is required after RA signaling (48 vs. 43 hpf). Moreover we know from previous study that a lack of FGF signaling does not abolish pitx2a expression in the tooth bud (10). B) Phylogenetic tree of the main fish models showing the presence of absence of a particular set of teeth (oral vs. pharyngeal). Red branch represents the hijack of RA for tooth induction in zebrafish.