Figure 1.
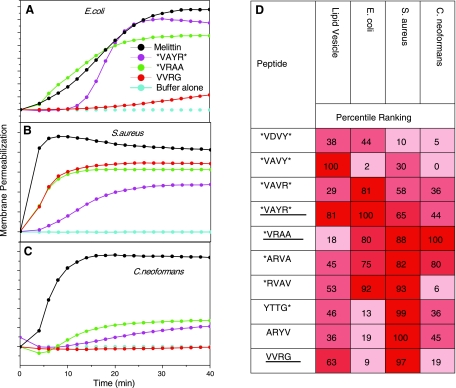
Cross characterization of the membrane-permeabilizing activity of vesicle-selected peptides. A–C) Examples of fluorescence of the membrane-impermeant, DNA-binding dye Sytox Green as a measure of biomembrane permeabilization in E. coli (A), S. aureus (B), and C. neoformans (C). Peptides are added at 5 μM to cells, and the fluorescence of Sytox Green is monitored for 40 min. Control for complete permeabilization is 5 μM melittin, a membrane-permeabilizing peptide from bee venom. Experiments for three example peptides in the three different organisms are shown. All permeabilization data are shown in Supplemental Table 1. D) Percentile-ranked permeabilization of vesicles at peptide:lipid ratio of 1:50 or microbes at 5 μM peptide and 107 bacteria/ml or 105 fungi/ml. Permeabilization is measured at 40 min, by which time the leakage had essentially ceased for vesicles and bacteria. Fungal permeabilization was linear and much slower (12). Cells in the table are colored by quartiles for visualization. Underlined peptide names are the example peptides in A–C.