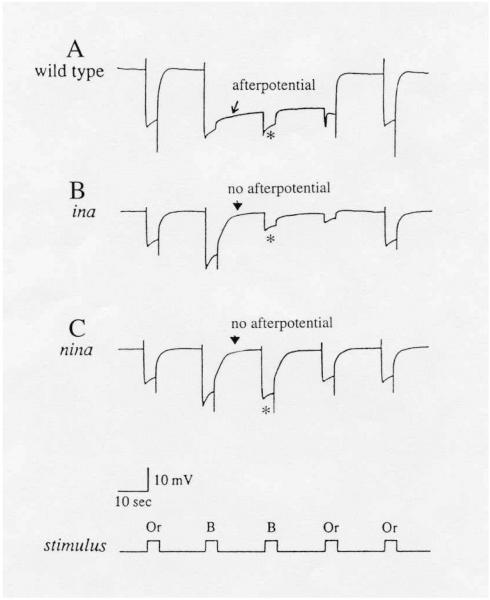
Figure 5.
ERG's of PDA-defective mutants, ina (inactivation but no afterpotential) (B) and nina (neither inactivation nor afterpotential) (C), compared to that of wild type (A).
A bright blue stimulus elicits the prolonged depolarizing afterpotential (PDA) in wild type (arrow in A), but not in ina (arrowhead in B) or nina (arrowhead in C) mutants. A second bright blue stimulus delivered during the PDA elicits only a small response, originating from R7 and R8 photoreceptors, in wild type and ina (* in A & B). The R1-6 photoreceptors are inactivated and do not respond. By contrast, in nina mutants, R1-6 photoreceptors are not inactivated and respond with a full amplitude response to the second blue stimulus (* in C). All flies were marked with white (w) or brown;scarlet (bw;st) to eliminate the screening pigments in pigment cells. Or: orange; B: blue. Reproduced from Pak and Leung (2003) with permission from Taylor & Francis, Inc.