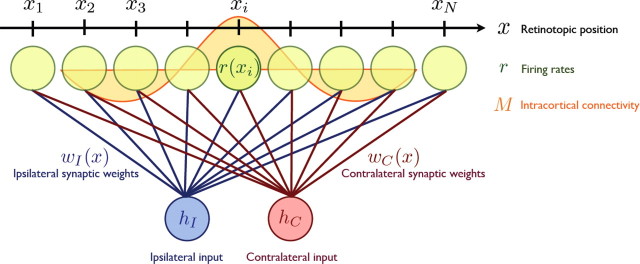
Figure 1.
A schematic figure of the model. N cortical neurons are lined up on a one-dimensional axis x. Each neuron receives feedforward input from both ipsilateral and contralateral eyes, and those synapses are modified according to activity-dependent plasticity rules. The intracortical connectivity, M, is a function of the distance between two cortical positions and changes its profile at the onset of the critical period when cortical inhibition matures.