Figure 1.
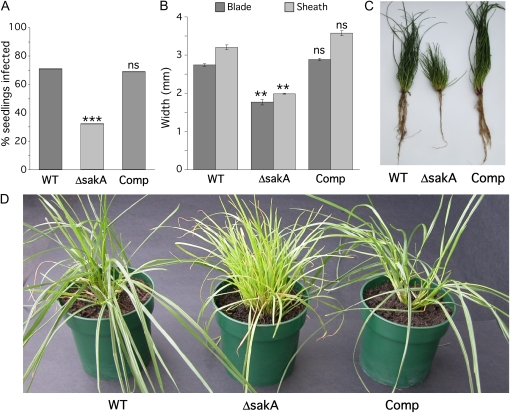
Symbiotic phenotype of the E. festucae ΔsakA mutant. A, Infection rate analysis for perennial ryegrass inoculated with E. festucae wild-type (WT), ΔsakA mutant, and complemented (Comp) strains. Bars represent average infection rates after multiple trials (n = 265, 282, and 200 for wild-type, ΔsakA, and Comp strains, respectively). Statistical significance in comparison with the wild-type strain was determined using the χ2 test (ns, not significant; ** 0.01 ≥ P > 0.001; *** P < 0.001). B, Average tiller widths of plants infected with wild-type, ΔsakA, and Comp strains. Measurements were taken just above the ligule on the blade (dark shading) and just below the ligule on the sheath (light shading). Error bars are se for two independent experiments (n = 50 for all strains). Reductions in blade and sheath widths were determined using a one-tailed Student's t test. C and D, Tiller and root phenotypes of perennial ryegrass infected with wild-type, ΔsakA, and Comp strains. These photographs were taken 12 weeks after inoculation. Yellowing of ΔsakA mutant-infected tillers indicates the onset of senescence.