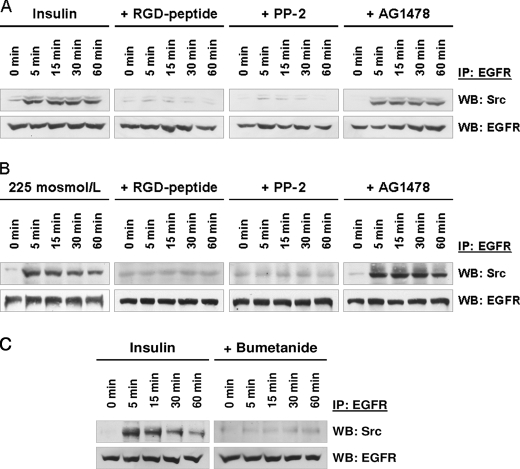
FIGURE 6.
Insulin- and hypoosmolarity-induced EGFR/c-Src association in perfused rat liver. Rat livers were perfused as described under “Experimental Procedures.” When indicated, RGD peptide (10 μmol/liter), PP-2 (250 nmol/liter), AG1478 (1 μmol/liter), or bumetanide (5 μmol/liter) was added 30 min prior to the institution of either insulin (35 nmol/liter; A and C) or hypoosmolarity (225 mosmol/liter, B). Liver samples were taken at the time points indicated, and EGFR was immunoprecipitated (IP) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Samples were then analyzed for EGFR/c-Src association by detection of c-Src. Total EGFR served as a loading control. Within 5 min both insulin (A) and hypoosmolarity (B) induced an EGFR/c-Src association, which lasts for up to 60 min. This EGFR/c-Src association was sensitive to inhibition of the integrin system (RGD peptide) or inhibition of c-Src kinase activity (PP-2), indicating that insulin- (A) or hypoosmolarity-induced (B) and integrin-mediated c-Src-activation (15, 16) is required for EGFR/c-Src association. Bumetanide also inhibited insulin-induced EGFR/c-Src association (C), underlining the importance of insulin-induced hepatocyte swelling for these processes. WB, Western blotting.