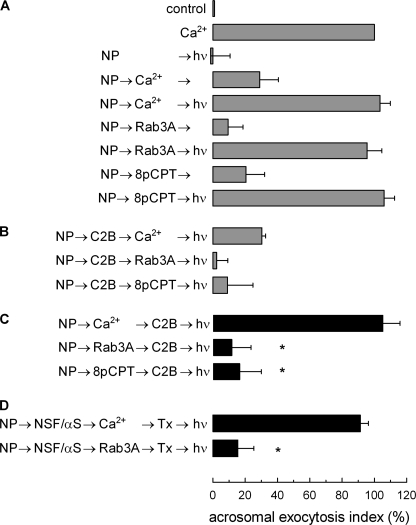
FIGURE 1.
Role of calcium during early stages of acrosomal exocytosis. Permeabilized spermatozoa were loaded with 10 μm NP-EGTA (NP) for 15 min at 37 °C to chelate intra-acrosomal Ca2+. Acrosomal exocytosis (AE) was then initiated by adding 10 μm free Ca2+, 300 nm Rab3A, or 50 μm 8pCPT. After a further 10 min of incubation at 37 °C to allow exocytosis to proceed up to the intra-acrosomal Ca2+-sensitive step, sperm were treated for 10 min at 37 °C with 500 nm synaptotagmin VI C2B domain (C2B). All of these procedures were carried out in the dark. UV flash photolysis of the chelator was induced at the end of the incubation period (hν), and the samples were incubated for 5 min to promote exocytosis. Relevant experimental conditions are shown as black bars in C. Control experimental conditions shown in A (gray bars) include background AE in the absence of any stimulation (control); AE stimulated by 10 μm free Ca2+; no effect of the combination of NP and light; inhibitory effect of NP-EGTA in the dark; and the recovery upon illumination when AE was initiated with Ca2+, Rab3A, or 8pCPT. Control conditions in B show the inhibitory effect of the C2B domain when included from the beginning of the experiment. In D, after loading the acrosome with NP-EGTA, the sperm were stimulated in the presence of 310 nm NSF plus 500 nm αSNAP (NSF/αS) with Ca2+ or Rab3A, and then 100 nm tetanus toxin (Tx) was added to cleave SNARE (specifically VAMP) molecules not assembled in SNARE complexes. UV flash photolysis of the chelator was induced at the end of the incubation period (hν), and the samples were incubated for 5 min to promote exocytosis. The sperm were fixed, and AE was measured. The percentage of reacted sperm was normalized as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The data represent the means ± S.E. of at least three independent experiments. The asterisks indicate significant differences from similar conditions stimulated with Ca2+ (p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA and Dunnett test).