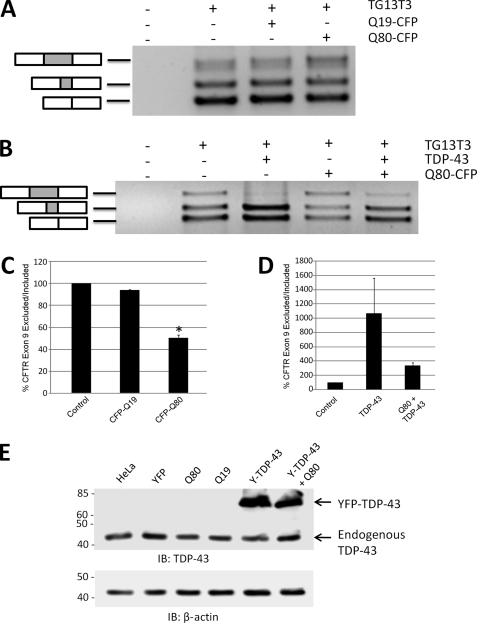
FIGURE 6.
Sequestration of nuclear TDP-43 into polyglutamine aggregates suppresses TDP-43-mediated splicing. To assess whether sequestration of TDP-43 into polyglutamine aggregates had an effect on TDP-43 function, HeLa cells were transfected with a CFTR minigene construct (TG13T3) as a reporter of TDP-43-mediated splicing. In the presence of endogenous TDP-43 levels in HeLa cells, three bands are observed, corresponding to exon 9 inclusion (upper band) or skipping of exon 9 (lower two bands). The middle band is due to the adoption of a cryptic splice acceptor site in exon 9, and the bottom band is from complete exon 9 skipping. A, co-transfection of TG13T3 with Q80-CFP increased exon 9 inclusion, consistent with a loss of basal levels of TDP-43-mediated exon 9 skipping by sequestration into polyQ aggregates. B, overexpression of TDP-43 strongly suppressed exon 9 inclusion (upper band) and enhanced exclusion (lower bands). The alteration in splicing of the CFTR exon 9 minigene induced by Q80-CFP was largely normalized by overexpression of TDP-43. C and d,, mean ratio of exon 9 exclusion/inclusion from three independent experiments, normalized to basal level in HeLa cells (control). *, p < 0.05, paired t test, control versus Q80-CFP. E, immunoblot (IB) of HeLa cell lysates with antibodies to TDP-43, showing that total TDP-43 levels were not affected by transfection with the polyQ-CFP constructs or the YFP-TDP-43 (Y-TDP-43) fusion protein. β-Actin immunoblot is shown below as a loading control.