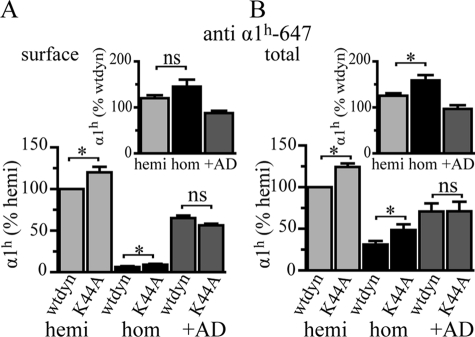
FIGURE 5.
Inhibiting dynamin-mediated endocytosis on the dominant effect of the α1(AD) subunit. We transfected HEK293T cells with 0.250 μg of β2 and γ2S subunit cDNA and either 0.125 μg of human wild type α1h subunit (hemi, light gray), 0.250 μg of human α1(AD)h subunit (hom, black), or 0.125 μg of human wild type α1h subunit and 2 μg α1(AD)r subunit (+AD, dark gray). In addition, we also co-transfected the cells with either 0.375 μg of wild type (wtdyn) or dominant negative (K44A) dynamin. We measured surface and total human α1 subunit expression by flow cytometry and normalized each value to the expression of the hemizygous samples that were co-transfected with wild type dynamin. In the insets, we plotted the percentage change in α1h and α1(AD)h expression because of the K44A dynamin. The K44A dynamin increased the total and surface α1 subunit expression in the hemizygous and homozygous conditions (p < 0.05), but not alter the dominant effect in the +α1(AD)r condition (n = 5). The K44A dynamin significantly increased total homozygous α1(AD)h expression to a greater extent than hemizygous α1h expression (p < 0.01). ns = p ≥ 0.05; *, p < 0.05.