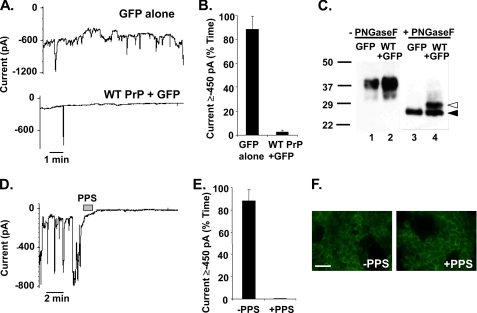
FIGURE 3.
ΔCR PrP-induced current is eliminated by overexpression of WT PrP and by treatment with PPS. A, whole-cell patch clamp recordings were made from HEK cells expressing ΔCR PrP at 48 h after infection with lentivirus encoding GFP alone (upper trace) or WT PrP plus GFP (lower trace). The holding potential was −80 mV. B, quantitation of the currents recorded in panel A, plotted as the percentage of total time the cells exhibited inward current ≥450 pA (mean ± S.E., n = 5 cells). C, cells in panel A were analyzed for PrP by Western blotting. Samples in lanes 3 and 4 were enzymatically deglycosylated with N-glycosidase F (PNGaseF), whereas those in lanes 1 and 2 were not. Deglycosylated WT and ΔCR PrP are identified by white and black arrowheads, respectively. D, whole-cell patch clamp recordings were made from HEK cells expressing ΔCR PrP. During the period indicated by the bar (60 s), the cell was perfused with PPS at 100 μg/ml. E, quantitation of the currents recorded in panel D plotted as the percentage of total time the cells exhibited inward current ≥450 pA (mean ± S.E., n = 5 cells). F, surface immunofluorescence staining of PrP (green) on HEK cells expressing ΔCR PrP, with or without a 2-min treatment with PPS. Scale bar = 50 μm.