Abstract
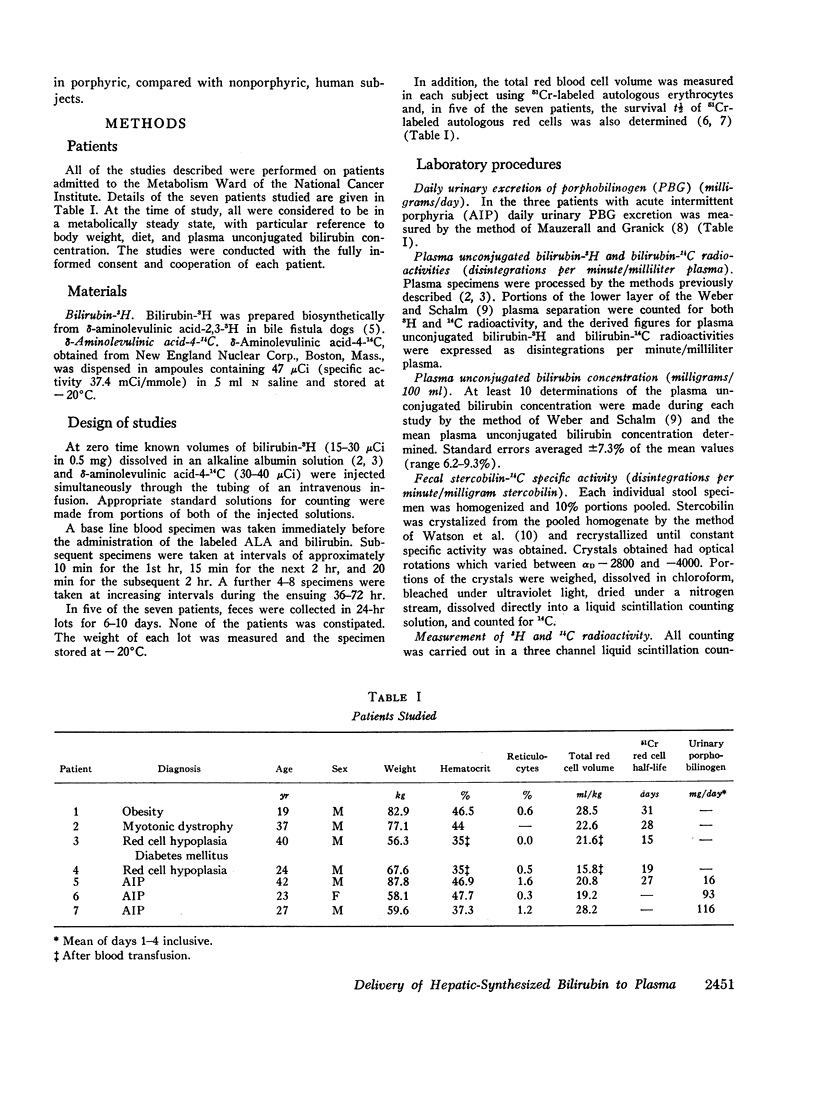
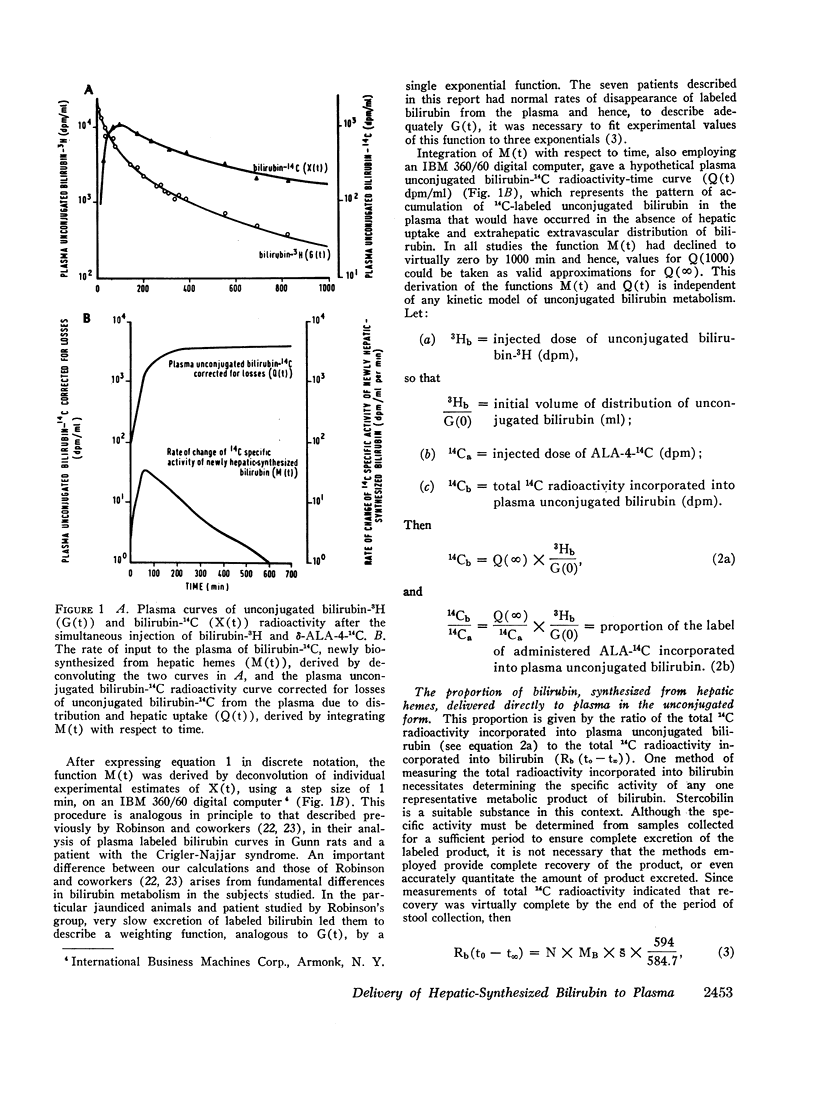
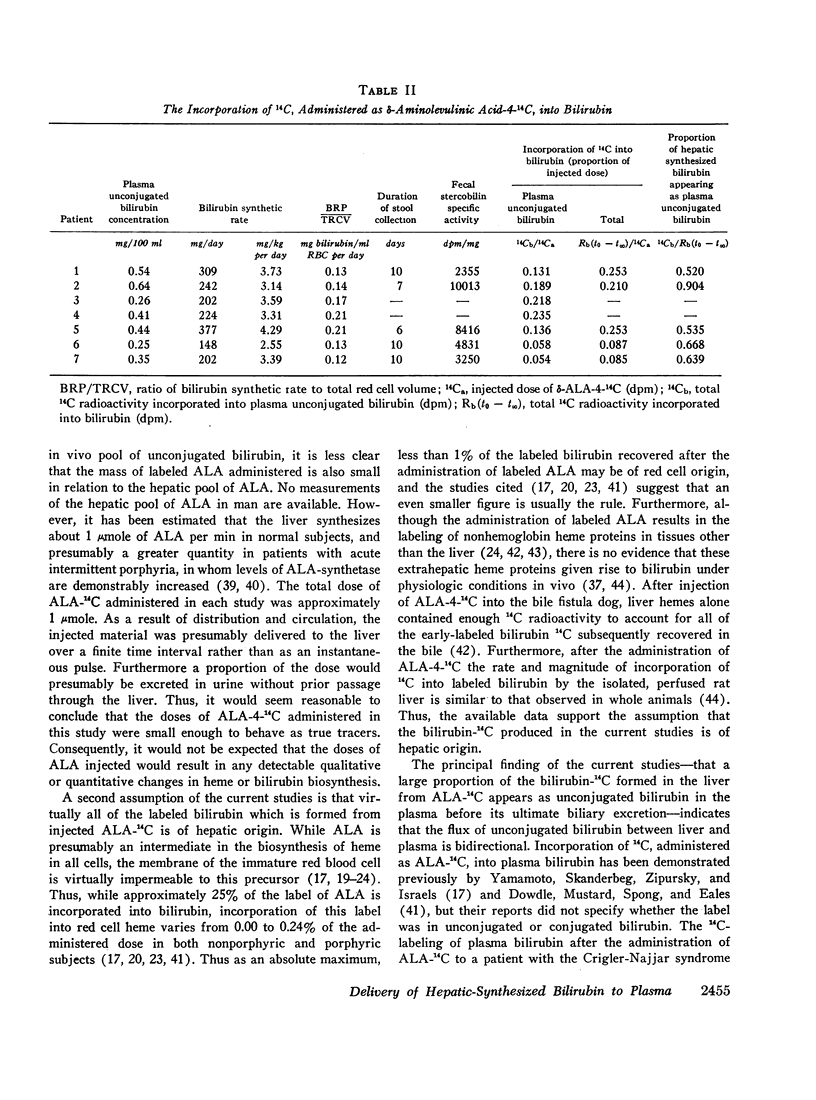
After the simultaneous intravenous administration of unconjugated bilirubin-3H and δ-aminolevulinic acid-4-14C, the plasma disappearance curves of unconjugated bilirubin-3H and the plasma appearance curves of biosynthesized unconjugated bilirubin-14C have been defined in seven patients, three of whom had acute intermittent porphyria (AIP). The incorporation of 14C into plasma unconjugated bilirubin, derived by an analysis which involves deconvolution of the two plasma curves, varied between 13.1 and 23.5% (mean 19.3%) of the injected dose in the nonporphyric patients and between 5.4 and 13.6% (mean 8.3%) of the injected dose in the porphyric patients. In five of the patients, the stercobilin-14C specific activity in a pooled specimen of feces was measured, enabling the following further values to be calculated: (a) the total 14C radioactivity incorporated into bilirubin (21.0 and 25.3% [mean 23.2%] of the injected dose in two of the nonporphyric patients and between 8.5 and 25.3% [mean 14.2%] of the injected dose in the porphyric patients), and (b) the proportion of hepatic synthesized bilirubin delivered directly to plasma in the unconjugated form (between 0.520 and 0.904; mean for nonporphyric patients 0.712; mean for porphyric patients 0.614). The results demonstrate that a large proportion of bilirubin derived from hepatic hemes passes through the plasma in the unconjugated form before conjugation and secretion into bile.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali M. A., Billing B. Plasma disappearance of conjugated and unconjugated C14 bilirubin in the rat with obstructive jaundice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Feb;124(2):339–342. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERLIN N. I., NEUBERGER A., SCOTT J. J. The metabolism of delta -aminolaevulic acid. 2. Normal pathways, studied with the aid of 14C. Biochem J. 1956 Sep;64(1):90–100. doi: 10.1042/bj0640090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BILLING B. H., WILLIAMS R., RICHARDS T. G. DEFECTS IN HEPATIC TRANSPORT OF BILIRUBIN IN CONGENITAL HYPERBILIRUBINAEMIA: AN ANALYSIS OF PLASMA BILIRUBIN DISAPPEARANCE CURVES. Clin Sci. 1964 Oct;27:245–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett P. V., Mullins F. X., Berlin N. I. Studies on the biosynthesis production of bilirubin-C14: an improved method utilizing delta-aminolevulinic acid-4-C14 in dogs. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Dec;68(6):905–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett V., Berk P. D., Menken M., Berlin N. I. Bilirubin turnover studies in normal and pathologic states using bilirubin-14C. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Feb;68(2):355–377. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-2-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk P. D., Bloomer J. R., Howe R. B., Blaschke T. F., Berlin N. I. Bilirubin production as a measure of red cell life span. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Mar;79(3):364–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk P. D., Howe R. B., Bloomer J. R., Berlin N. I. Studies of bilirubin kinetics in normal adults. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2176–2190. doi: 10.1172/JCI106184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomer J. R., Berk P. D., Bonkowsky H. L., Stein J. A., Berlin N. I., Tschudy D. P. Blood volume and bilirubin production in acute intermittent porphyria. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jan 7;284(1):17–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197101072840104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COBURN R. F., BLAKEMORE W. S., FORSTER R. E. Endogenous carbon monoxide production in man. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42:1172–1178. doi: 10.1172/JCI104802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKSON G. H., RIMINGTON C. Porphobilinogen. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):476–484. doi: 10.1042/bj0570476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Pharmacological implications of microsomal enzyme induction. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):317–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdle E., Mustard P., Spong N., Eales L. The metabolism of (5-14C)delta-aminolaevulic acid in normal and porphyric human subjects. Clin Sci. 1968 Apr;34(2):233–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORESKY C. A. INITIAL DISTRIBUTION AND RATE OF UPTAKE OF SULFOBROMOPHTHALEIN IN THE LIVER. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jul;207:13–26. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe R. B., Berk P. D., Bloomer J. R., Berlin N. I. Preparation and properties of specifically labeled radiochemically stable 3H-bilirubin. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Mar;75(3):499–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISRAELS L. G., YAMAMOTO T., SKANDERBEG J., ZIPURSKY A. Shunt bilirubin: evidence for two components. Science. 1963 Mar 15;139(3559):1054–1055. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3559.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. A., Bloomer J. R., Berlin N. I. The measurement of the synthetic rate of bilirubin from hepatic hemes in patients with acute intermittent porphyria. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2259–2265. doi: 10.1172/JCI106723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABBE R. F., NISHIDA G. A new method of hemin isolation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Nov;26(2):437–437. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landaw S. A., Callahan E. W., Jr, Schmid R. Catabolism of heme in vivo: comparison of the simultaneous production of bilirubin and carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):914–925. doi: 10.1172/JCI106311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M., Schacter B. A., Zipursky A., Israels L. G. The nonerythropoietic component of early bilirubin. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jun;47(6):1281–1294. doi: 10.1172/JCI105820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUZERALL D., GRANICK S. The occurrence and determination of delta-amino-levulinic acid and porphobilinogen in urine. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):435–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORELL D. B., STEWART M. The removal of iron from haemins. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1956 Jun;34(3):211–217. doi: 10.1038/icb.1956.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUBERGER A., SCOTT J. J. Aminolaevulinic acid and porphyrin biosynthesis. Nature. 1953 Dec 12;172(4389):1093–1094. doi: 10.1038/1721093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- READ R. C. Studies of red-cell volume and turnover using radiochromium; description of a new closed method of red-cell volume measurement. N Engl J Med. 1954 Jun 17;250(24):1021–1027. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195406172502402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. H. Increased bilirubin formation from nonhemoglobin sources in rats with disorders of the liver. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Apr;73(4):668–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. H., Lester R., Crigler J. F., Jr, Tsong M. Early-labeled peak of bile pigment in man. Studies with glycine-14C and delta-aminolevulinic acid-3H. N Engl J Med. 1967 Dec 21;277(25):1323–1329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196712212772501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. H., Owen C. A., Jr, Flock E. V., Schmid R. Bilirubin formation in the liver from nonhemoglobin sources. Experiments with isolated, perfused rat liver. Blood. 1965 Dec;26(6):823–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. H., Tsong M., Brown B. W., Schmid R. The sources of bile pigment in the rat: studies of the "early labeled" fraction. J Clin Invest. 1966 Oct;45(10):1569–1586. doi: 10.1172/JCI105463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID R., HAMMAKER L. METABOLISM AND DISPOSITION OF C14-BILIRUBIN IN CONGENITAL NONHEMOLYTIC JAUNDICE. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1720–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI104858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K., GRAY S. J. Determination of the circulating red cell volume in man by radioactive chromium. J Clin Invest. 1950 Dec;29(12):1614–1619. doi: 10.1172/JCI102404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Frohlich G., Schmidt D., Stich W. Der Urobilinkörperstoffwechsel des Menschen. I. Eine neue Methode zur Bestimmung der Urobilinkörper im menschlichen Serum und Harn. Blut. 1971 Mar;22(3):120–124. doi: 10.1007/BF01632201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand L. J., Felsher B. F., Redeker A. G., Marver H. S. Heme biosynthesis in intermittent acute prophyria: decreased hepatic conversion of porphobilinogen to porphyrins and increased delta aminolevulinic acid synthetase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1315–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSCHUDY D. P., PERLROTH M. G., MARVER H. S., COLLINS A., HUNTER G., Jr, RECHCIGL M., Jr ACUTE INTERMITTENT PORPHYRIA: THE FIRST "OVERPRODUCTION DISEASE" LOCALIZED TO A SPECIFIC ENZYME. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:841–847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON C. J., LOWRY P. T., SBOROV V. E., HOLLINSHEAD W. H., KOHAN S., MATTE H. O. A simple method of isolation of crystalline stercobilin or urobilin from feces. J Biol Chem. 1953 Feb;200(2):697–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER A. P., SCHALM L. Quantitative separation and determination of bilirubin and conjugated bilirubin in human serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1962 Nov;7:805–810. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(62)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman A. D., Berk P. D., Schalch D., Tschudy D. P. Isolated adrenocorticotrophic hormone deficiency in acute intermittent porphyria. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Feb;70(2):317–323. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-2-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAMOTO T., SKANDERBEG J., ZIPURSKY A., ISRAELS L. G. THE EARLY APPEARING BILIRUBIN: EVIDENCE FOR TWO COMPONENTS. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jan;44:31–41. doi: 10.1172/JCI105124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Fujii M., Inuki T., Wakisaka G. The incorporation of delta aminolaevulinic acid and glycine into faecal stercobilin and coproporphyrin in man. Br J Haematol. 1969 Jan-Feb;16(1):197–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


