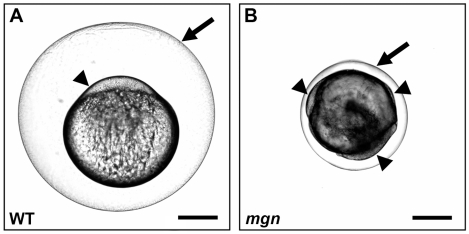
Figure 1. mgn is required for animal-vegetal polarity of the egg.
Nomarski images of eggs from a wild-type (heterozygous sibling) female (A) and a mgn mutant female (B) one hour post activation. Eggs from mgn mutants exhibit cytoplasm surrounding the yolk (arrowheads) rather than restricted to the blastodisc at the animal pole as in wild-type (lateral view, animal pole up). In addition, mgn eggs are frequently smaller and display variable elevation of the chorion (arrow). Scale bar = 250 microns.