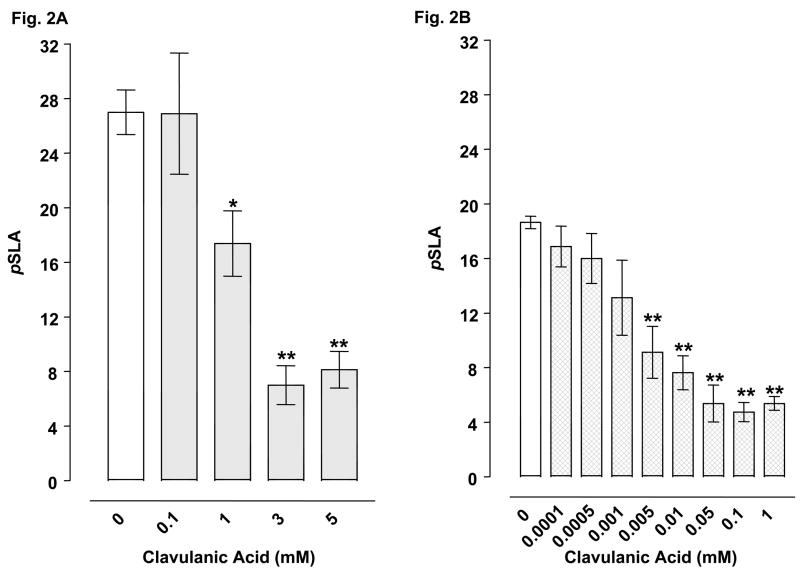
Fig. 2.
Effects of clavulanic acid on pSLA induced by 3 mM glutamate (2A) or 3 mM cocaine (2B). Planarians were treated for 5 min with glutamate or cocaine by itself or in combination with clavulanic acid. Data are expressed as mean pSLA ± S.E.M. versus concentration of clavulanic acid. Main effects are indicated on the panels. **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05 compared to the glutamate or cocaine alone group (i.e., clavulanic acid concentration of 0 mM) following identification of significant main effects for the clavulanic acid/glutamate [F(4, 35) = 13.58, p < 0.0001] and clavulanic acid/cocaine [F(8, 64) = 12.77, p < 0.0001] data sets. N = 8 planarians per group.