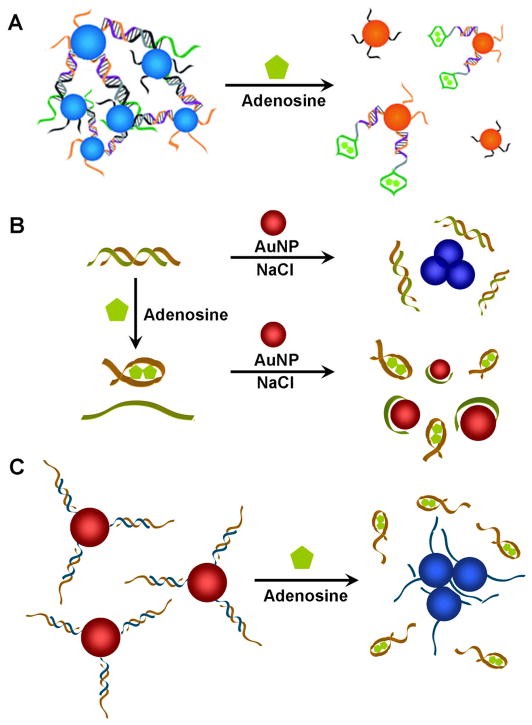
Fig. 4.
Aptamer-AuNP based colorimetric sensors. (A) AuNPs functionalized with oligonucleotides have been used for labeled sensors. AuNPs are initially aggregated with adenosine specific aptamer strands. The introduction of adenosine stimulates disassembly of AuNPs, changing the color of AuNPs from blue to red. (B) The interaction between unmodified AuNPs and unlabeled ssDNA strand has been used to make label-free sensors. In the presence of adenosine, dsDNA containing an adenosine aptamer strand (brown) releases ssDNA (green) which can be adsorbed onto unmodified AuNPs. AuNPs remain dispersed with red color even in the presence of NaCl due to enhanced stability of AuNPs provided by ssDNA. In the absence of adenosine, dsDNA with adenosine aptamer strand stays hybridized. The electrostatic repulsion between dsDNA and AuNP as well as the stiffness of dsDNA make them ineffective in preventing NaCl induced charge screening on AuNP surface, causing aggregation of AuNPs with color change from red to blue. (C) Both labeled and label-free method has been combined to make an adenosine sensor. AuNPs are chemically functionalized with DNA (blue) and hybridized with adenosine aptamer strand (brown). In the presence of adenosine, aptamer strands are released from AuNPs decreasing the stability of AuNPs. The resulting aggregation of AuNPs induces color change from red to blue.