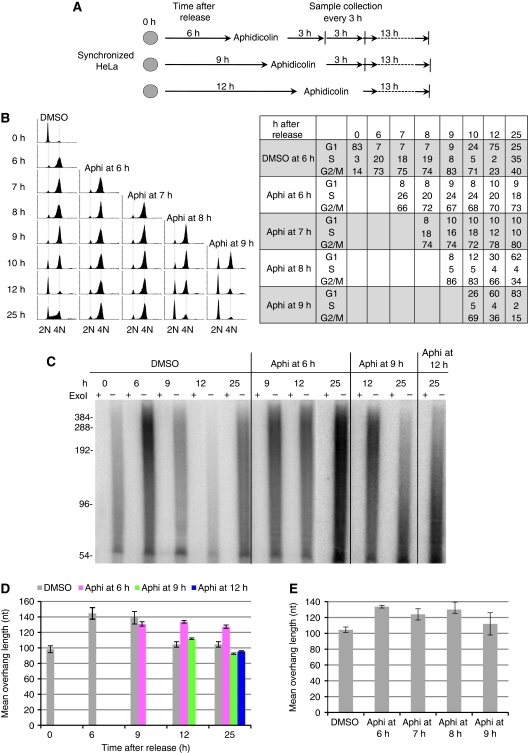
Figure 5.
The lagging strand synthesis machinery is required for C-strand fill-in. (A) Diagram of aphidicolin inhibition. (B) FACS analysis shows that inhibiting polα activity at late S or G2 phase arrested cells in G2 phase. HeLa was synchronized at G1/S boundary and then released into S phase. Aphidicolin (aphi) was added at different times during the cell cycle. Cells were arrested at G2 phase when polα was inhibited in late S/G2 phase (6 h) or G2 phase (7 and 8 h), whereas the cell cycle progression was delayed when aphidicolin was added at late G2/M phase (9 h). Percentage of cells at each phase of the cell cycle is shown next to the FACS profile. (C) G-overhangs remained elongated when polα activity was inhibited at G2 phase. Aphidicolin was added at late S/early G2 (6 h after release), late G2/M (9 h after release), or after G2/M (12 h after release) to inhibit polα activity. Cells were collected at 9, 12, and 25 h and G-overhang sizes were measured using overhang protection assay. ExoI digests 3′ overhangs and the ExoI plus (+) lanes show the background. (D) The weighted mean sizes of G-overhangs from (C). Results are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars represent s.d. (E) Excessive G-overhangs were produced upon polα inhibition at G2 phase. After synchronization of HeLa at G1/early S boundary, aphidicolin or DMSO was added at different times during the cell cycle and cells were collected at 12 h after release.