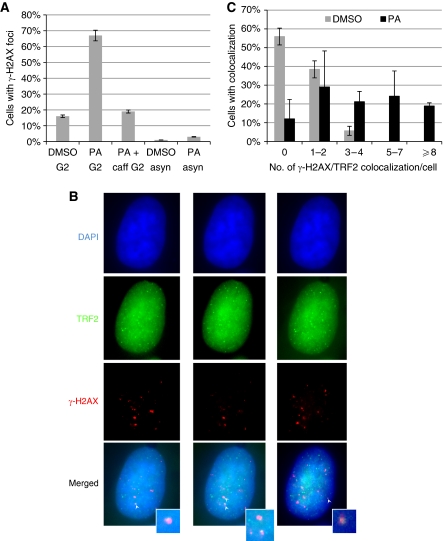
Figure 7.
Inhibition of CDK1 at late S/G2 leads to DNA damage response at telomeres. (A) Increased ATM/ATR-dependent DNA damage response upon CDK1 inhibition at G2 phase. PA was added at 2 h after the G1/S arrested HeLa was released into S phase. Cells were fixed at 9 h (G2 phase) for anti-γ-H2AX immunostaining (PA G2). Caffeine was added at 6 h after release (PA+caff G2). A total of over 100 cells in random fields were counted for each sample and cells containing >4 γ-H2AX foci were considered as positive. Treatment of asynchronized HeLa PA for 9 h (PA asyn) did not significantly increase γ-H2AX staining. Results are from two experiments. (B) Representative images showing colocalization of γ-H2AX with TRF2. Cells were stained with antibodies specific for TRF2 (green) and γ-H2AX (red), and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Cells were optically sectioned at 0.275 μM intervals, and colocalizations (yellow) were observed in multiple sections. Here, sections from the same nucleus containing colocalization (indicated by white arrow) are shown, and inserts show enlarged images of colocalization. (C) Percent of cells containing TRF2/γ-H2AX colocalization. A total of over 50 nuclei were analysed for each sample. Results are average from three experiments. Error bars represent s.d. A full-colour version of this figure is available at The EMBO Journal Online.