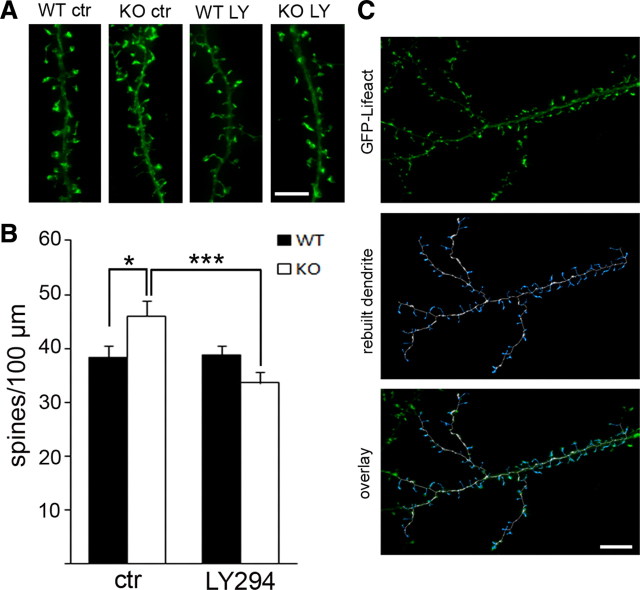
Figure 7.
A PI3K antagonist rescues increased dendritic spine density in Fmr1 KO neurons. A, Three-dimensional reconstruction of representative dendrites from WT and Fmr1 KO neurons (18 DIV) after 3 d of treatment with vehicle (ctr) or LY294002 (LY, 10 μm) illustrates that increased protrusion density in Fmr1 KO is rescued by PI3K inhibition. Scale bar, 5 μm. B, Automated quantification using FilamentTracer software (Imaris, Bitplane) shows significantly increased protrusion density in vehicle-treated Fmr1 KO, which can be restored to WT levels by LY294002 treatment, but does not change spine morphology in WT. Bar diagrams represent average spine number per 100 μm (WT control, 38.2; WT LY294002, 38.7; KO control, 46.0; KO LY294002, 33.6; n = 30, 2 independent cultures, two-way ANOVA: significant interaction between genotype and treatment, *p = 0.001; LSD post hoc tests: *p wtctr–koctr = 0.024, ***p koctr–koLY294002 < 0.0001, p wtctr–wtLY294002 = 0.996; error bars represent SEM). C, Examples of a dendrite that was analyzed with FilamentTracer (Imaris; Bitplane) illustrate accuracy of the applied method to identify protrusions. Top, Three-dimensional reconstruction of fluorescent signals from GFP–Lifeact transfected hippocampal dendrite; middle, traced and rebuilt dendrite (white) with spines (blue); bottom, overlay of rebuilt dendrite with original image. Scale bar, 10 μm.