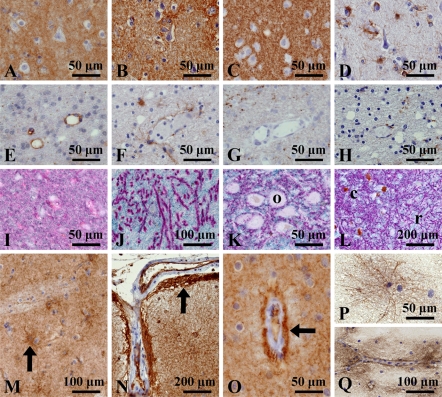
Figure 4.
A comparative study of expression of S1PR1, synaptophysin, aquaporin 4 (AQP4), and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in cerebrum (A–L) and expression of S1PR1 in astrocyte morphology (M–Q). (A–D) Cerebral cortex and (E–H) cerebral white matter. At high-power magnification, the gray matter shows diffusely fine granular staining of S1PR1 (A) similar to those of AQP4 (B) and synaptophysin (C), whereas the white matter shows focal faint staining of S1PR1 (E), AQP4 (F), and synaptophysin (G). GFAP-positive astrocytes are loosely distributed in both cortex (D) and white matter (H). Nerve cell bodies do not stain for S1PR1. Double immunostaining of synaptophysin (red) and S1PR1 (blue) demonstrated a fine intermingled distribution pattern of these antigens in the cerebral cortex (I). In the globus pallidus, a clear differential distribution pattern is seen (J). In the midbrain, differential localization is seen in oculomotor nucleus (K) and substantia nigra (L). Astrocytes with radial cytoplasmic processes in the putamen are stained (M). The glia limitans of the brain surface (N) and blood vessels (O) show strong expression. Radial elongated cytoplasmic staining is clearly seen in the squash preparation, by ICC (P). Immunoreaction products are localized around the blood vessels (Q). o, oculomotor nerve; c, substantia nigra pars compacta; r, substantia nigra pars reticulata.