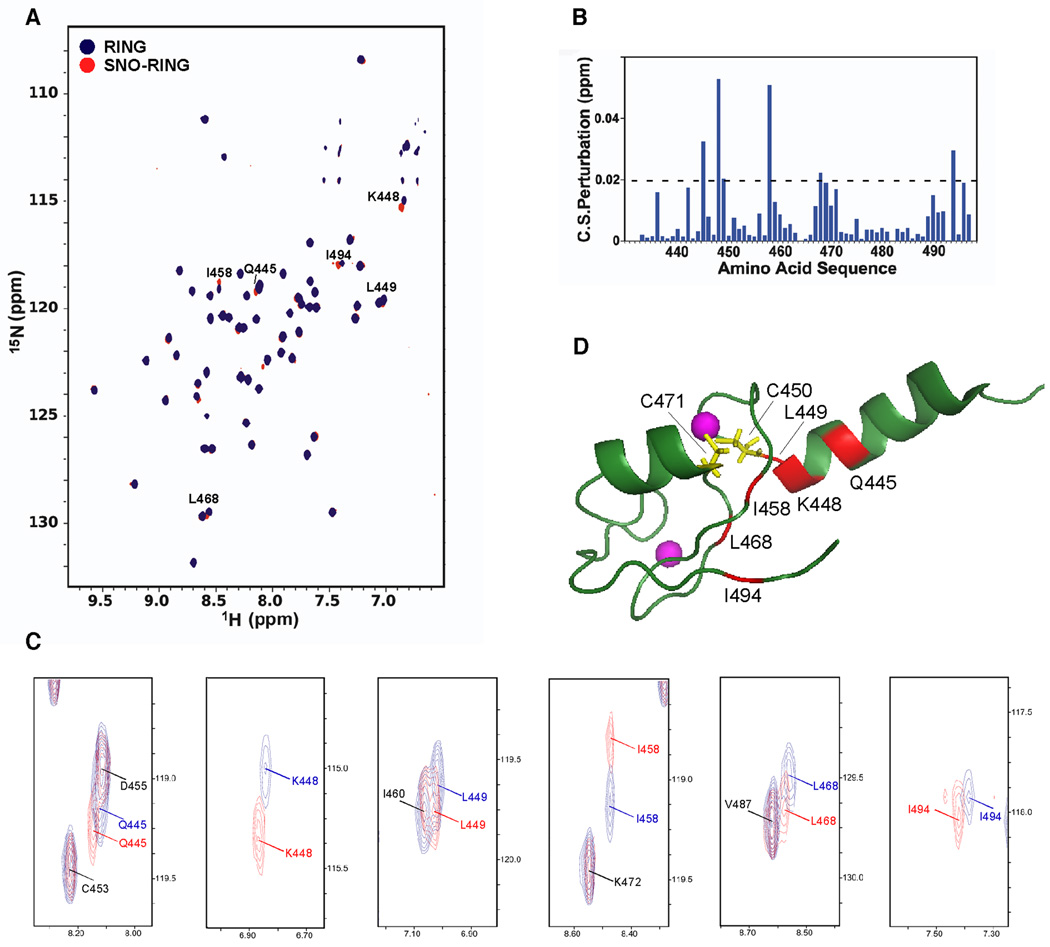
Figure 2. NMR Analysis of the XIAP-RING Domain.
(A) [1H-15N] TROSY NMR spectra of native and S-nitrosylated XIAP-RING domain. Chemical shift (CS) differences are shown between native RING (RING; blue) and S-nitrosylated RING (SNO-RING; red). Cross peaks with significant CS changes caused by S-nitrosylation (>0.02 ppm) are labeled with one letter amino-acid codes.
(B) CS perturbations induced by S-nitrosylation versus amino acid sequence.
(C) Higher-powered views of cross peaks with significant CS changes caused by S-nitrosylation (>0.02 ppm). Cross peaks are marked in either red (S-nitrosylated form) or blue (native form). Cross peaks without significant CS changes (<0.02 ppm) are labeled with black one letter amino-acid codes.
(D) NMR structure of XIAP-RING domain (PDB: 2ECG). Residues manifesting CS changes after S-nitrosylation are displayed in red (>0.02 ppm). Two cysteines (C450 and C471) located proximate to the chemically shifted/perturbed residues are colored yellow.