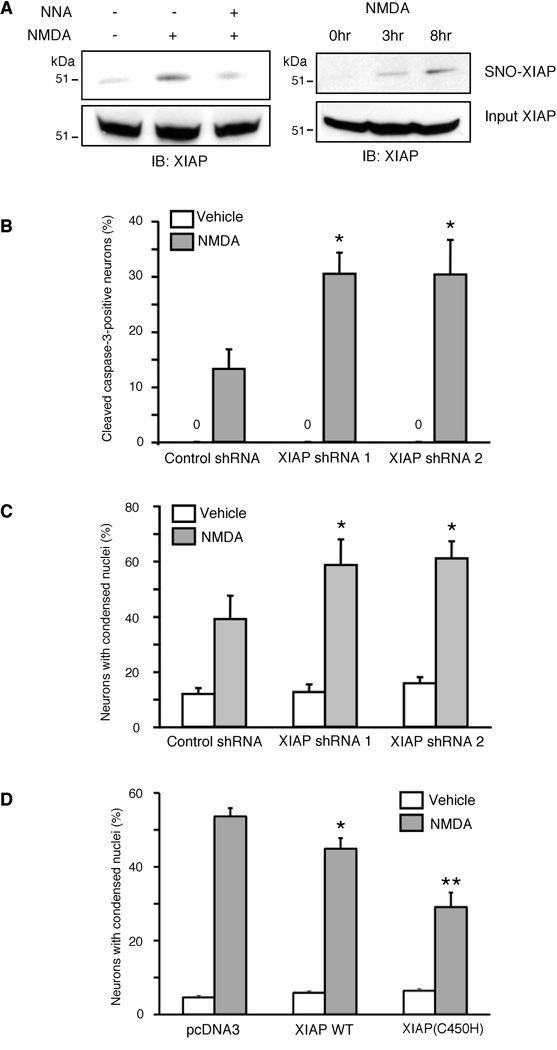
Figure 6. XIAP Provides Neuroprotection from NMDAR-Mediated Excitotoxicity.
(A) SNO-XIAP was detected in cultured rat cerebrocortical neurons after exposure to NMDA by NO-biotin switch analysis. The NOS inhibitor NNA inhibited the formation of SNO-XIAP.
(B, C) Reduction of XIAP levels by shRNA sensitizes cortical neurons to NMDA. Cortical neurons were transfected with shRNAs, exposed to NMDA, and after 6 hr immunostained with anti-NeuN (to identify neurons) and anti-cleaved caspase-3 (to detect active caspase-3). The percentage of active caspase-3-positive neurons increased in XIAP shRNA-transfected neurons compared to control neurons (B). In parallel, the number of apoptotic neurons increased 8–14 hr later (C).
(D) Enhanced antiapoptotic activity of XIAP(C450H). Cortical neurons were transfected with XIAP or XIAP(C450H), exposed to NMDA, and after 12 hr immunostained with anti-NeuN. Apoptotic cell death was monitored by counting the number of Hoechst-stained nuclei containing condensed/fragmented chromatin (n ≥ 500 neurons scored in 3 independent experiments; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 by ANOVA). Data are presented as mean + SEM.