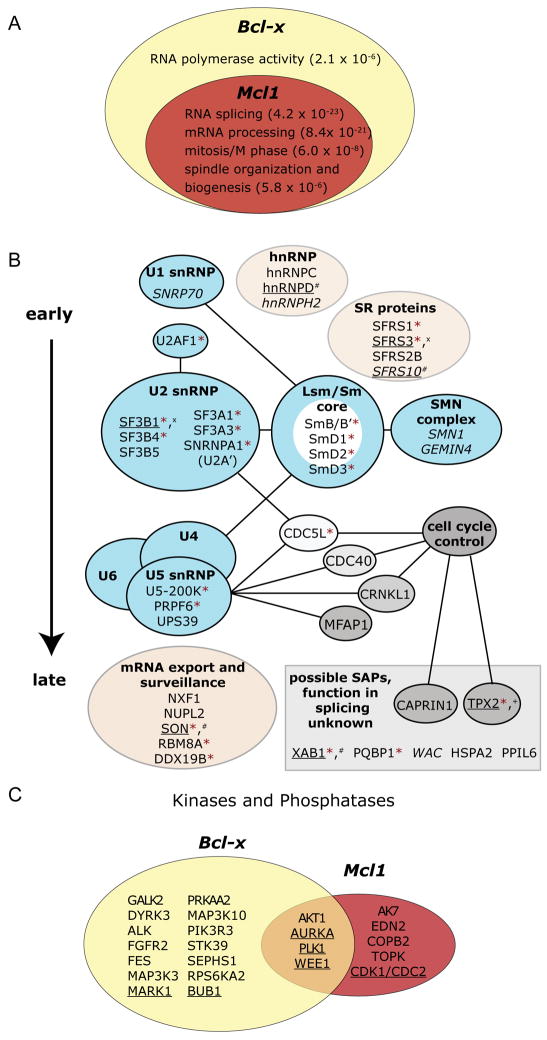
Figure 4. Coordinated regulation of Bcl-x and Mcl1 alternative splicing.
(A) Bcl-x screen hits were tested for Mcl1 regulation to identify common regulators. High confidence hits are depicted as a Venn Diagram, with GO enrichments listed with p-values in the subsets where they were most significantly enriched (see Figure S4 and Table S4).
(B) Spliceosome-associated proteins that were Bcl-x screen hits are shown with established physical interactions and functional roles. Blue ellipses represent known RNP or protein complexes; pink ellipses contain functionally or structurally related factors. Low-confidence hits are italicized. Factors in gray rectangle have unknown roles in splicing, but were identified in proteomic analyses or are similar to known splicing factors (Chen et al., 2007). Factors are marked as follows: * = high-confidence hit for Mcl1; underlined = phosphorylated in mitosis; + = putative AURKA target; x = putative CDK1 target; # = putative PLK1 target (Dephoure et al., 2008).
(C) Hits from a kinase/phosphatase screen for Mcl1 splicing regulation are shown, with corresponding Bcl-x regulators. A cutoff of p<10−5 in three replicates, or p<10−7 in two replicates was applied (see Table S5). Cell cycle factors are underlined.