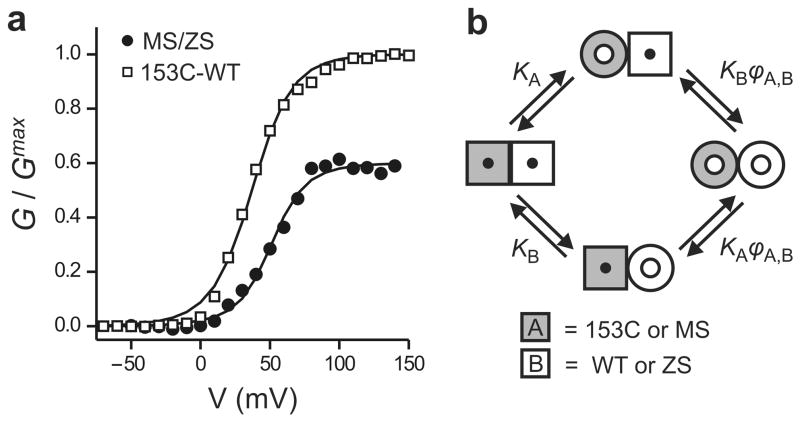
Figure 4.
Quantification of cooperativity in Hv1. (a) Voltage dependence of activation of the MS/ZS heterodimer and the 153C-WT linked dimer fitted with the opening model shown in b. For MS/ZS Hv1: ϕMS,MS = ϕMS,ZS = ϕZS,ZS = 60 ± 35, for153C-WT Hv1: ϕ153C,153C = ϕWT,WT = 95, ϕ153C,WT = 23 ± 2. See text for details. (b) Model of opening of the two pores of Hv1. Cooperativity is quantified by the parameter ϕ, which is the ratio between the open probability of a given subunit when the neighboring subunit is in the open conformation and the open probability of the same subunit when the neighboring subunit is in the closed conformation. ϕ > 1 means that the opening of one pore makes it easier for the other pore to open (positive cooperativity). The scheme represents the case of a heterodimer made of subunit A (gray) and subunit B (white) with different voltage dependencies of activation (KA and KB). Subunit A can be 153C or MS, and subunit B can be WT or ZS. The transition from square shape to round shape represents the conformational change associated with opening (see also Supplementary Fig.4).