Figure 6.
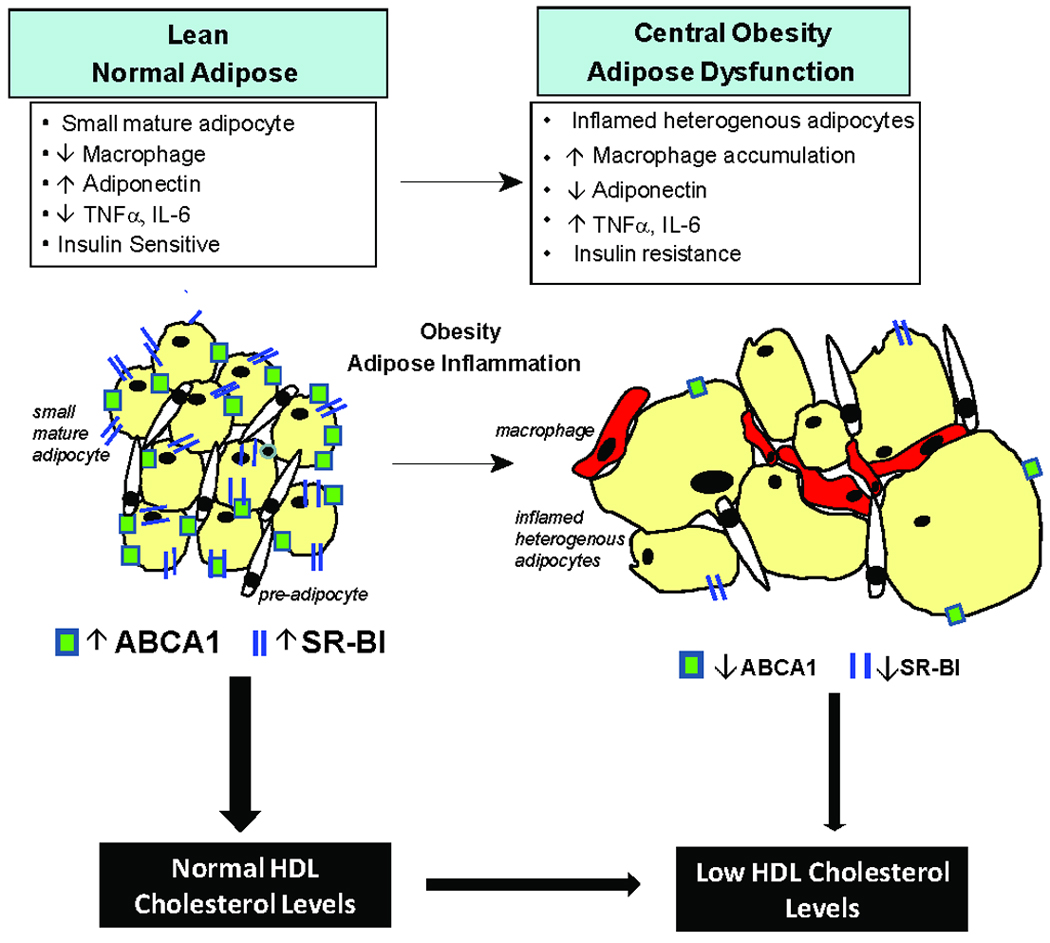
As adipose inflammation is a hallmark of central obesity and type-2 diabetes, loss of adipocyte lipidation of HDL may directly contribute to lower HDL-C levels in these inflammatory, insulin resistant states. Despite greater adipose mass and cholesterol content in adiposity, adipocyte inflammation is associated with reduced expression of the cholesterol efflux transporters, ABCA1 and SR-BI, and impaired cholesterol efflux to apoA-I and HDL particles.
