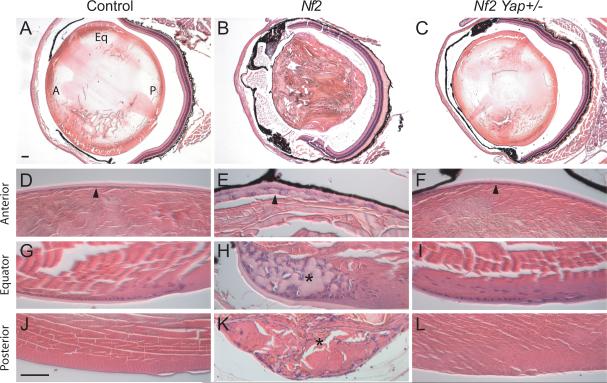
Figure 5. Yap heterozygosity suppresses cataracts induced by loss of Nf2.
(A–C) H&E staining of lens from 2-month old littermates with the following genotypes: (A) Nf2flox2/flox2 (as control), (B) Nes-Cre; Nf2flox2/flox2, and (C) Nes-Cre; Nf2flox2/flox2; Yapflox/+. Note the general loss of structural integrity in (B), but not in (A) or (C). In (A), the anterior, equator and posterior regions of lens are marked by A, Eq and P, respectively.
(D–L) High magnification views of lens in (A–C) highlighting anterior, equator and posterior regions of the lens. Note the disorganization of anterior lens epithelium in Nes-Cre; Nf2flox2/flox2, and the normal monolayer cuboidal epitheliaium in Nes-Cre; Nf2flox2/flox2; Yapflox/+ lens (compare arrowheads in D–F). Also note the accumulation of ectopic cells and capsular material at the equator region of Nes-Cre; Nf2flox2/flox2 (asterisk, H), but not Nes-Cre; Nf2flox2/flox2; Yapflox/+ (I) lens. Furthermore, the posterior lens, which is normally accellular (J; appearing as hematoxylin-negative), shows abberant accumulation of cells in Nes-Cre; Nf2flox2/flox2 (asterisk, K), but not Nes-Cre; Nf2flox2/flox2; Yapflox/+ (L) lens.
Scale bars = 100 μm.