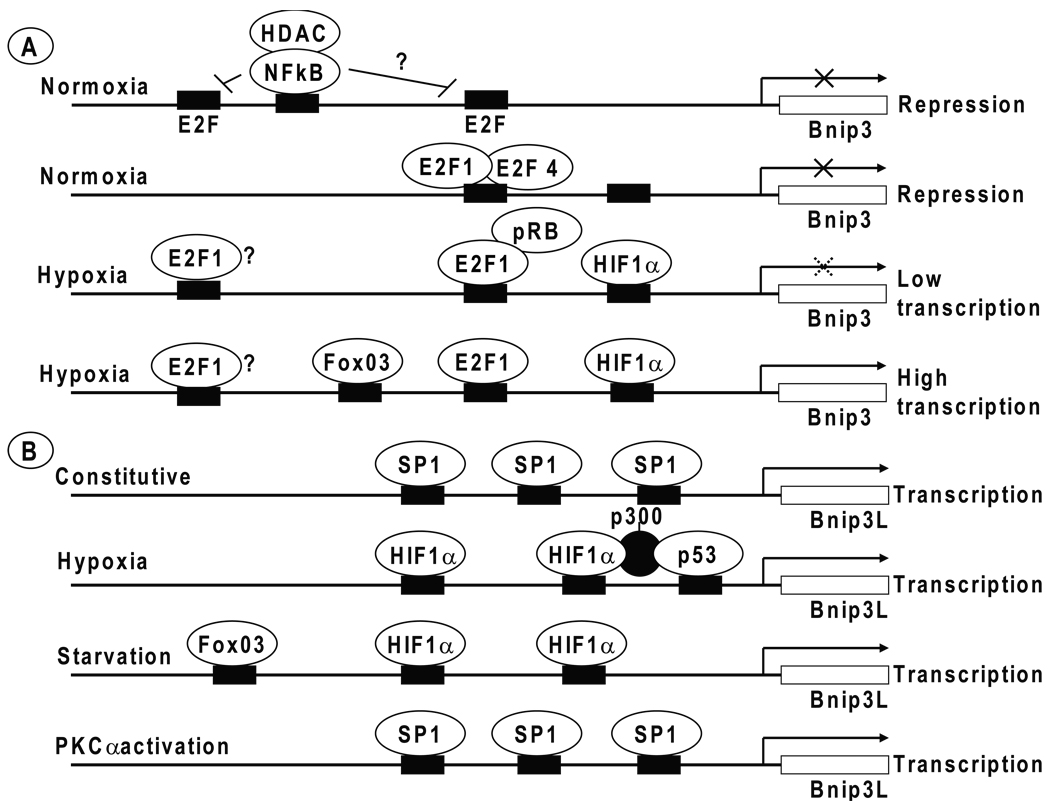
Fig. 3. Transcriptional regulation of Bnip3 and Bnip3L.
(A) The transcription of the Bnip3 gene is depicted to be repressed under normoxic conditions by transcription factors NFκB and E2F4. Under hypoxia, the activity of HIF1α is shown to be moderated by the negative regulatory effects of pRb and NFκB. Hypoxia-induced high level transcription appears to be mediated by the combined action of E2F1 and/or FoxO3 with HIF1α. (B) In contrast to Bnip3, expression of Bnip3L is constitutive in several tissues and is shown to be mediated by transcription factors such as Sp1. Under hypoxic conditions, p53 is shown to cooperatively activate transcription with HIF1α. Similarly, under conditions of starvation, the transcription is shown to be activated by FoxO3, possibly in cooperation with HIF1α. Under specific conditions such as cardiac hypertrophy that results in PKCα activation, the transcription is indicated to be activated by Sp1. The context under which the various transcription factors may regulate transcription of Bnip3 and Bnip3L is discussed in the text. The binding sites for various transcription factors are indicated by solid bars (not all sites are shown).