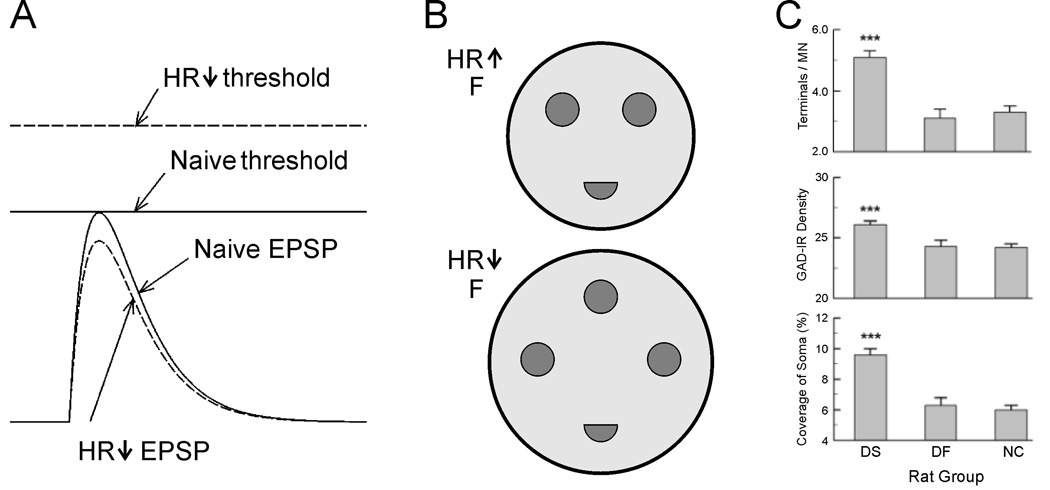
Figure 2.
Spinal cord plasticity induced by H-reflex conditioning. A: Motoneurons have more positive firing thresholds and tend to have smaller Ia EPSPs after H-reflex down-conditioning.17 As a result, they are less likely to fire in response to nerve stimulation. B: Schematic showing that down-conditioned monkeys have bigger F terminals than up-conditioned monkeys, and that their F terminals have more active zones.21 C: Soleus motoneurons of successfully down-conditioned rats (DS) have more detectable GAD67-labeled terminals, higher density of GAD immunoreactivity, and larger GAD-terminal coverage of soma than those of naive control rats (NC) or unsuccessful down-conditioned rats (DF). 22