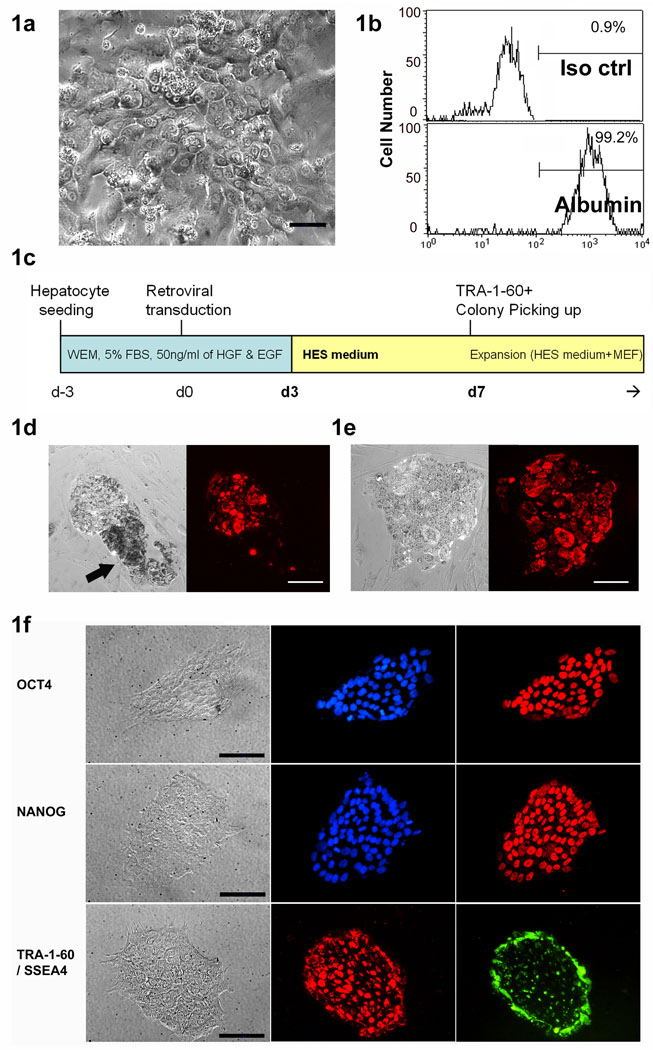
Figure 1. Human hepatocyte derived iPS (hHiPS) cell colony formation and characterization.
(a) Phase contrast image and (b) albumin expression of primary human hepatocytes before iPS reprogramming. ×200, Scale bars: 50 µm. (c) A diagram of hHiPS generation protocol. (d) Typical example of a small ES cell–like TRA-1-60 (red) positive colony adjacent to a TRA-1-60 negative non-iPS colony (arrow). (e) Typical ES cell–like TRA-1-60 positive iPS cell colony before harvest. ×100, Scale bars: 100 µm. (f) Representative immunofluorescence analysis of one hHiPS cell line (hHiPS10) growing on Matrigel. Clear expression of the ES cell surface antigens SSEA4 and TRA-1-60, the nuclear transcription factors OCT4 and NANOG are observed (×200). Scale bars: 50 µm.