Figure 1.
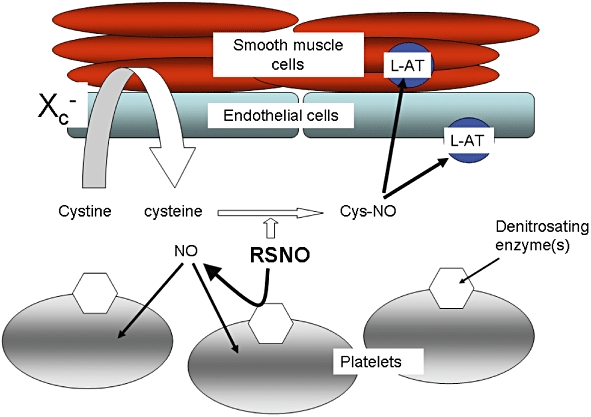
Different modes of nitric oxide (NO) delivery from S-nitrosothiols (RSNOs). Cells of the vascular wall import NO principally via uptake of S-nitrosocysteine (cysNO) on the amino acid transporter system L (L-AT), following an extracellular process of transnitrosation from RSNO to cysteine. A cystine–cysteine shuttle mediated by the Xc- transporter may act as a supply of extracellular reduced cysteine. In contrast NO delivery into platelets relies on the activity of cell surface denitrosating enzymes, such as cell surface isomerases (csPDI). This scheme indicates the main routes of NO uptake, but does not exclude the possibility that alternative or additional routes are available for each cell type.
