Figure 6.
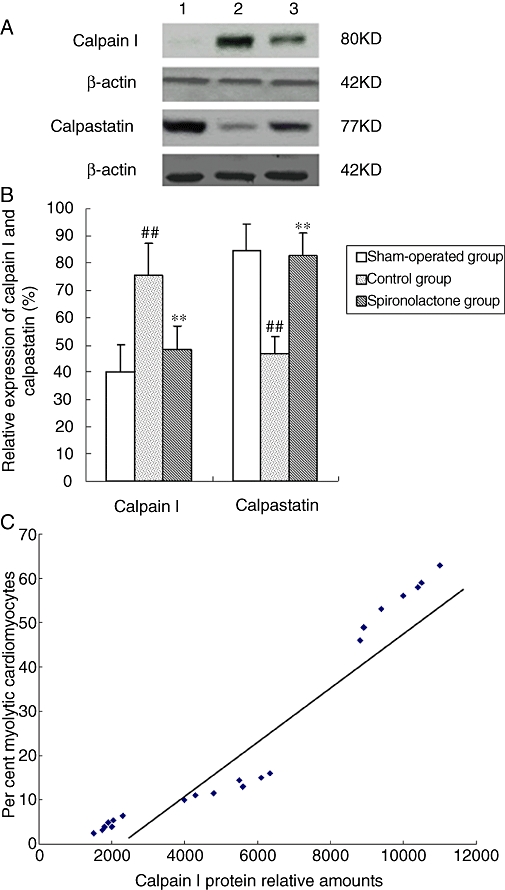
(A) Expression of calpain I and calpastatin analysed by Western blot. (B) Bars represent relative densitometric calpain I and calpastatin protein ratios. Arial myocardium subjected to chronic pacing for 6 weeks revealed a significant increase in calpain I and a decrease in calpastatin expression, compared with sham-operated group. The increase of calpain I and the decrease of calpastatin were significantly attenuated by spironolactone. ##P < 0.01, compared with the sham-operated group; **P < 0.01, compared with the control group. (C) The relationship between the expression of calpain I and percentages of myolytic myocytes. The myolytic cardiomyocytes were the total cardiomyocytes with mild and severe myolysis. Tissue calpain protein amounts correlated with the degree of myolysis in the sham-operated group, control group and spironolactone group (r= 0.91, P < 0.05).
