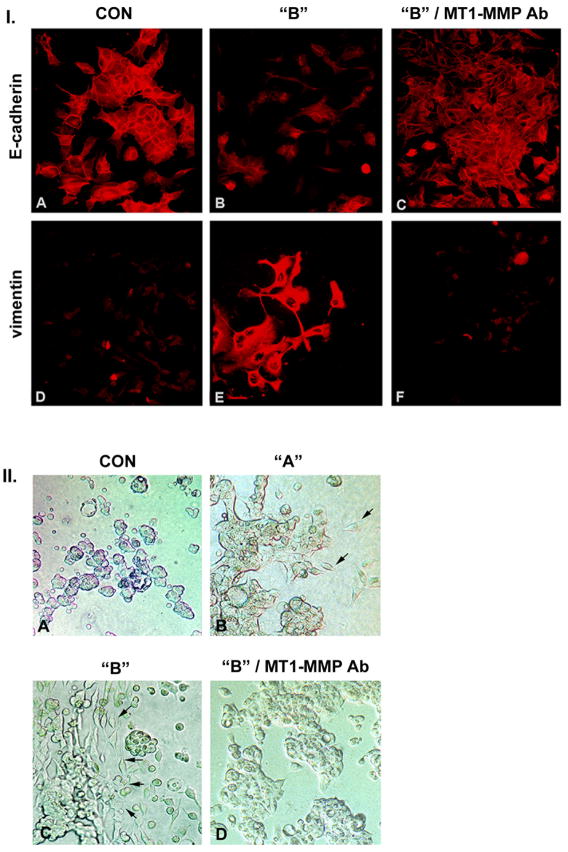
Figure 2. YB-1 transfected MCF-7 cells undergo epithelial to mesenchymal transition.
I. The epithelial marker E-cadherin is reduced in YB-1-EGFP transfected cells (B) as compared to control cells (A) and has a primarily cytosolic distribution. Incubation with a monoclonal antibody directed against the catalytic site of MT1-MMP reverts the YB-1 transfected cells to a normal epithelial phenotype with restitution of E-cadherin expression (C). Staining for vimentin reveals the contrary pattern with detection of vimentin in cells over expressing YB-1-EGFP (E) compared to control cells (D). With inclusion of the antibody targeting the catalytic MT1-MMP site the vimentin expression is down regulated (F). Magnification 450-fold.
II. YB-1 promotes invasive activity of MCF-7 cells in three dimensional collagen gels. Control MCF-7 cells grow in multicellular spherules (A). Population “A” cells grow primarily in spherules with occasional single cells invading the collagen gel (B), while population “B” cells are present as elongated individual cells with cohort or invasion front characteristics (arrows) (C). Inclusion of monoclonal anti-MT1-MMP antibody in the collagen gel reverts population “B” MCF-7 cells to an epithelial, non-invasive phenotype (D). Magnification 200-fold.