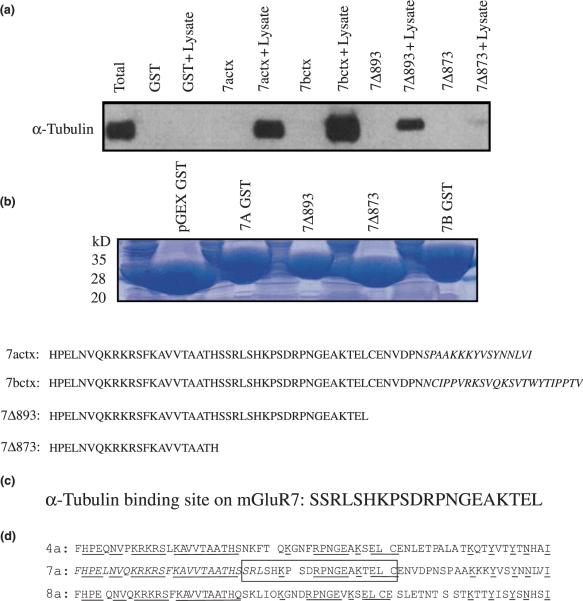
Fig. 4.
Characterization of the alpha tubulin-binding site on mGluR7. An immunoblot shows that both mGluR7a and mGluR7b CT fusion proteins bind to tubulin and suggests that the splice variant regions (15 and 23 terminal amino acids, respectively) are not necessary for alpha tubulin-binding (a). Deletion mutagenesis experiments show that the deletion mutant mGluR7Δ893 (expressing residues 851–892) binds to alpha tubulin while the deletion mutant mGluR7Δ873 (expressing residues 851–872) does not (a). A Coomassie stained 4–20% SDS–polyacrylamide gel shows that each of the GST fusion proteins used in the pull-down assay were expressed in equal amounts (b). The results indicate that alpha tubulin binds to a region of the mGluR7 CT domain between amino acid residues 873 and 892 (c). The group-III CT domains are depicted; the conserved amino acid residues are underlined, the alpha tubulin-binding site is boxed, the calmodulin/Gβγ-binding site and PKA/PKC phosphorylation sites are italicized (d).