Fig. 5.
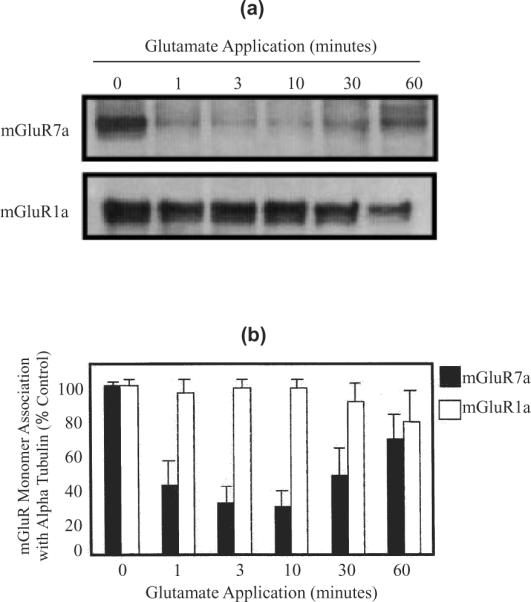
mGluR7a receptor activation regulates the alpha tubulin interaction. Immunoblots show that the monomeric form of mGluR7a receptors coimmunoprecipitate with alpha tubulin when mGluR7a-expressing BHK cell lysate is incubated with anti-alpha tubulin polyclonal antibody. However, mGluR7a binding to alpha tubulin is significantly reduced when the cells are incubated with 2 mM glutamate (a). In contrast, identical blots probed with an anti-mGluR1a antibody reveal that the regulation of alpha tubulin-binding is specific for mGluR7a. Bar graph shows the densitometry analysis of representative immunoblots using NIH Image 1.62. There is a 58% decrease in the mGluR7a association with alpha tubulin within one minute and a maximal decrease in binding (72%) at 10 min of glutamate application. However, there is no significant decrease in the binding of mGluR1a and alpha tubulin (b). These results suggest that there is a specific and dynamic regulation of the interaction between alpha tubulin and mGluR7. n = 3 for each experiment, error bars show the standard deviation.
