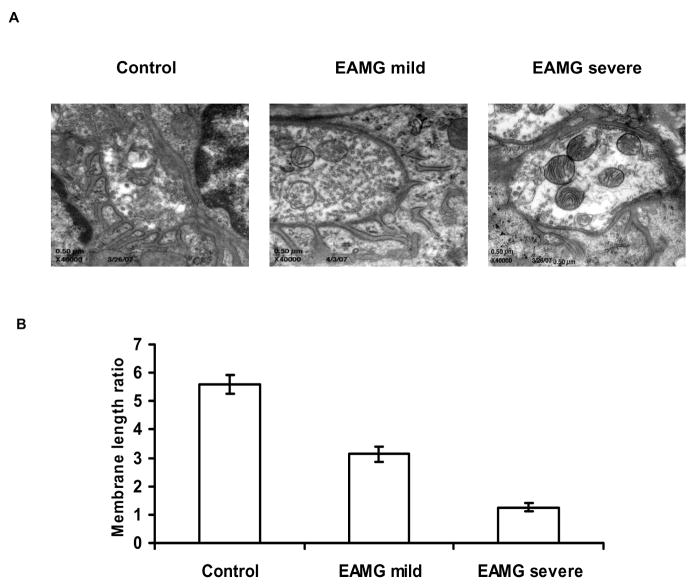
Figure 3.
A. Electron microscopic examination of postsynaptic folds of motor endplates in EAMG mice. Representative NMJ from a control animal shows normal morphology with characteristic “folding” of the postsynaptic membrane. This morphology is largely preserved in mice with mild EAMG, as illustrated in a representative NMJ from a mouse with mild EAMG. Mice with severe disease (and upregulation of AChR-α) showed morphological abnormalities characterized by simplification of the membrane structure and reduction or loss of the postsynaptic folding pattern. B. Quantitative analysis of the ultrastructure of neuromuscular junctions in muscle tissue from normal mice, mild EAMG, and severe EAMG. Postsynaptic membrane length (PostSM) to presynaptic membrane length (PreSM) ratios were calculated in the three experimental groups and average ratio values are shown in the graph, indicating a markedly reduced (PostSM)/(PreSM) ratio in mice with severe EAMG.