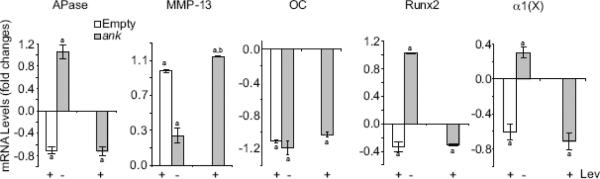
Figure 5.
The effect of elevated extracellular PPi and/or Pi levels on mRNA levels of hypertrophic and terminal differentiation markers, including APase, MMP-13, osteocalcin (OC), runx2, and type X collagen (α1(X)). To elevate extracellular PPi levels and prevent extracellular PPi hydrolysis to Pi, empty vector-transfected growth plate chondrocytes were cultured in the presence of levamisole (+ Lev) to inhibit APase activity. In addition, growth plate chondrocytes were transfected with pcDNA expression vector containing full-length ank cDNA (ank) and cultured in the presence of levamisole (+ Lev) for 2 days after transfection. To increase local extracellular Pi concentrations generated by ANK and APase, growth plate chondrocytes were transfected with pcDNA expression vector containing full-length ank cDNA (ank) in the absence of levamisole (− Lev). The levels of hypertrophic and terminal differentiation marker mRNAs, including APase, MMP-13, osteocalcin (OC), runx2, and type X collagen (α1(X)), were determined by real-time PCR and SYBR Green and normalized to the 18S RNA levels. Data are means of triplicate PCRs using RNA from three different cultures, and expressed as fold changes compared to untreated growth plate chondrocytes transfected with empty vector (Empty); error bars represent standard deviations (ap < 0.01 vs. cells transfected with empty vector; bp < 0.01 vs. cells transfected with empty vector and treated with levamisole).