Fig. 1.
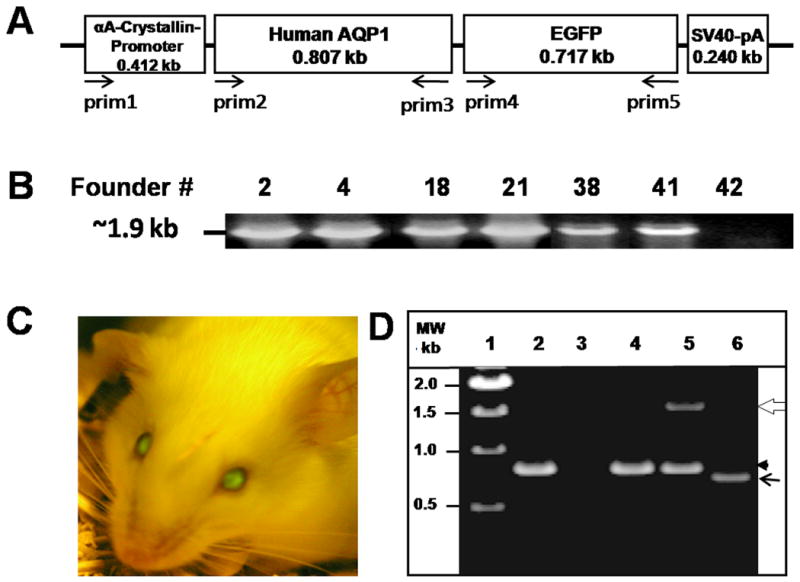
Generation and characterization of transgenic AQP1 (TgAQP1) mouse. A. Physical map of the construct used for generating AQP1-EGFP transgenic mice. Lens fiber cell-specific transgene construct containing αA-crystallin promoter, the coding region of human AQP1, an in-frame fluorescent epitope tag (EGFP) at the C-terminus of human AQP1 and SV40 polyA signal. Arrows indicate orientation and approximate location of the PCR primers. B. Genotyping to identify heterozygous transgenic founder mice. DNA from tail biopsies of pups (# 2, 4, 18, 21, 38, 41 and 42) was extracted and PCR method was used to detect the transgenics using sense (prim1) and anti-sense (prim5) primers. A band of 1.9 kb corresponding to the promoter + AQP1 + EGFP was amplified from the genomic DNA of each of the pups except for # 42. C. Identification of homozygous transgenic mouse (# 38) expressing EGFP in the lens, using Dark Reader. D. Examination of the expression of AQP1 and/or AQP1-EGFP transcripts in WT and TgAQP1+/+ lenses using RT-PCR. Lane 1, Molecular weight marker; lane 2, WT lens epithelial cells; lane 3, WT lens fiber cells; lane 4, TgAQP1+/+ epithelial cells; lanes 5 and 6, TgAQP1+/+ fiber cells. White open arrow, 1500 bp segment of AQP1-EGFP; black arrowhead, 800 bp segment of AQP1; black arrow, 700 bp segment of EGFP.
