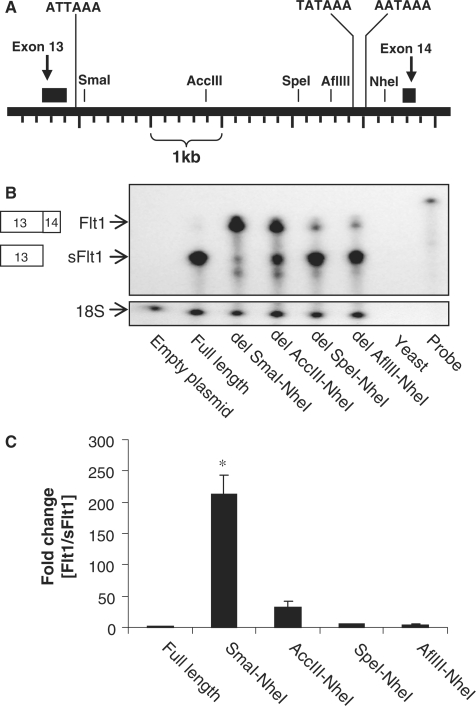
Figure 3.
Mapping cis-elements within intron 13 that regulate the relative abundance of intronic sFlt1 and Flt1. (A) Schematic representation of human FLT1 gene in the region of exons 13 and 14. Exon 13 splices to exon 14 to form Flt1; alternatively, intronic polyadenylation sites are used to create a composite 3′ terminal exon for sFlt1. The position of the putative proximal poly(A) signal sequence, the known distal poly(A) signal sequences and the restriction sites used to map cis-elements are shown. (B) RPA demonstrating relative abundance of intronic sFlt1 and spliced Flt1 in COS-7 cells transfected with a series of Flt1 minigene constructs. The full-length construct leads primarily to intronic sFlt1, and the largest deletions leads primarily to spliced Flt1. Progressive 5′–3′ deletions lead to a fall in processed Flt1. (C) Pooled quantitated data from several experiments with the Flt1 to sFlt1 ratio in each condition expressed as fold increase compared to the ratio in the full-length construct. n = 3, mean ± SEM, *P < 0.01, ANOVA (by ranks).