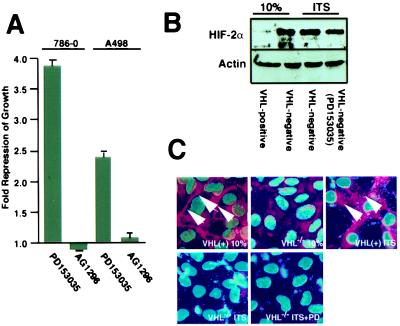
Figure 4.
Effects of EGF-R tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment on the growth of VHL−/− RCC cells in low serum. (A) Proliferation of VHL−/− RCC cells treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors was measured by BrdUrd labeling. Cells were plated overnight in DMEM supplemented with 10% FCS, washed, and then incubated in DMEM supplemented with ITS in the presence of either PD153035 (1 μM) or AG1296 (50 μM) for 48 h. BrdUrd was added during the last 3 h before analysis. Cells were then fixed and stained with anti-BrdUrd and Hoecsht reagent. Ratios of BrdUrd-positive nuclei/Hoecsht-stained nuclei were compared with VHL−/− RCC cells incubated for 48 h in ITS. Shown is the mean of three fields counted for at least three independent experiments; the SEM is indicated. (B) VHL−/− RCC cells and VHL-positive cells were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% FCS, ITS, or ITS and PD153035 (1 μM) for 48 h. HIFα levels were determined by immunoblot analysis. (C) VHL−/− RCC cells and VHL-positive cells were grown at confluency in DMEM supplemented with 10% FCS, ITS, or ITS and PD153035 (1 μM) for 6 days. Nuclear areas were revealed by Hoecsht stain, and fibronectin deposition was determined by immunofluorescence and is identified by arrows. Images were superimposed with the use of adobe photoshop.