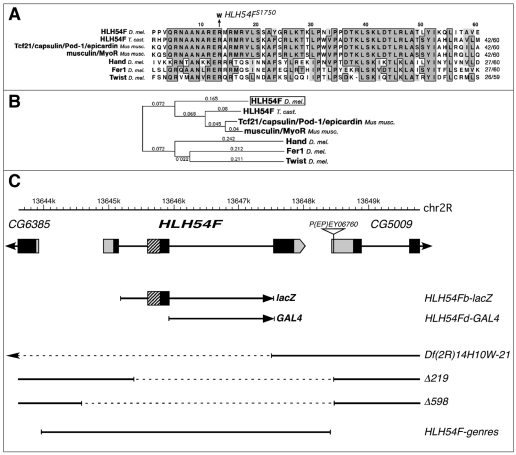
Fig. 1.
HLH54F protein sequence comparison, gene locus and mutations. (A) Alignment of the bHLH domain of HLH54F with the most closely related bHLH domains from mouse, Tribolium and Drosophila. The R-to-W exchange in the predicted protein from EMS allele HLH54FS1750 is indicated. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of data from A. (C) HLH54F gene map showing translated regions (black), the bHLH domain (hatched) and UTRs (gray). Beneath are shown the genomic regions used for the lacZ construct, GAL4 construct and the genomic rescue construct HLH54F-genres, as well as the molecularly defined breakpoints (dashed lines) of Df(2R)14H10W-21 and the P-excision alleles HLH54FΔ219 and HLH54FΔ598.