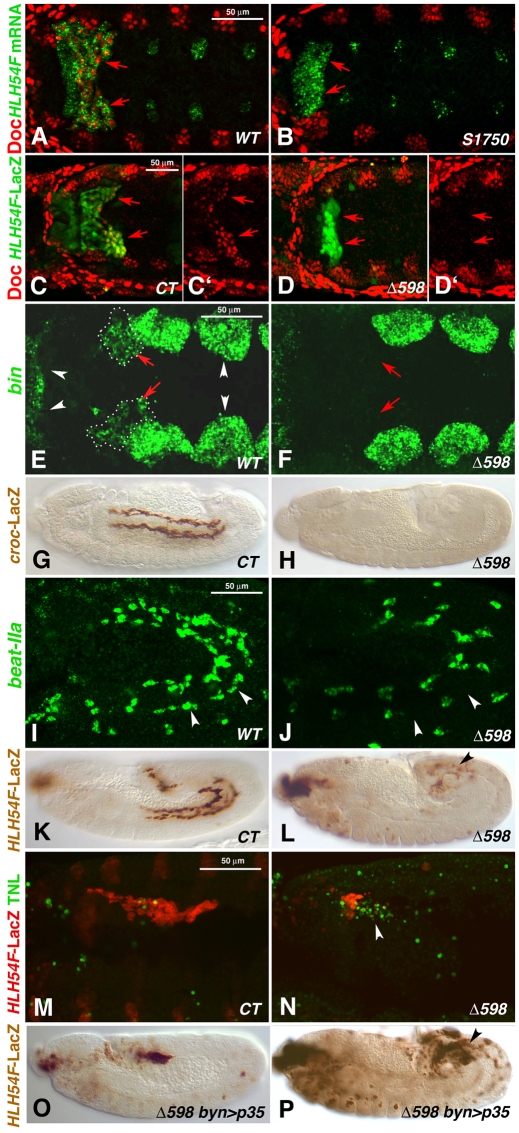
Fig. 4.
Embryonic HLH54F mutant phenotypes. (A,C,C′,E,G,I,K,M) Wild-type (WT) or control (CT) Drosophila embryos and (B,D,D′,F,H,J,L,N-P) HLH54F mutant embryos (alleles as indicated). (A-F) Dorsal views; (G-P) lateral views. (A) Stage 10 WT embryo stained for Doc protein in bilateral CVM clusters (arrows, red) and HLH54F mRNA (green). (B) HLH54FS1750 embryo stained as in A, which lacks Doc signals specifically in the CVM areas marked by mutant HLH54F mRNA (arrows). (C,C′) Stage 10 HLH54Fb-lacZ embryo stained for Doc protein (red, shown singly in C′) and β-gal (green) in CVM (arrows). (D,D′) HLH54FΔ598 embryo with HLH54Fb-lacZ stained as in C is missing Doc expression in β-gal-stained caudal mesoderm. (E) Late stage 10 WT embryo stained for bin mRNA in the CVM (red arrows, dotted outlines) and in TVM and HVM primordia (white arrowheads). (F) HLH54FΔ598 mutant, in which bin mRNA is missing in corresponding areas. (G) Stage 14 WT embryo expressing croc-lacZ in migrating CVM cells. (H) HLH54F; croc-lacZ mutant without croc-lacZ expression. (I) Stage 12 embryo showing beat-IIa mRNA in migrating CVM cells adjacent to the TVM (arrowheads) and in unidentified cells. (J) HLH54FΔ598 mutant embryo without beat-IIa mRNA signals adjacent to the TVM. (K) Stage 12 control embryo expressing HLH54Fb-lacZ in the migrating CVM. (L) Stage 12 HLH54FΔ598 mutant embryo expressing HLH54Fb-lacZ, showing a large decrease in the number of positive cells, which are not migrating (arrowhead). (M) Early stage 12 HLH54Fb-lacZ control embryo stained for β-gal (CVM, red) and by TUNEL assay (green), which shows few apoptotic cells in CVM areas. (N) Stage 12 HLH54FΔ598, HLH54Fb-lacZ mutant embryo with many TUNEL-positive cells (arrowhead). (O) Stage 11 HLH54FΔ598 mutant embryo expressing HLH54Fb-lacZ and byn-GAL4-driven anti-apoptotic p35 with normal numbers of internalized lacZ-positive cells (see Fig. 2D). (P) Stage 12 HLH54FΔ598 mutant embryo with apoptosis inhibition as in O and an increased number of HLH54Fb-lacZ-containing cells as compared with mutants without forced p35 expression (see L), which fail to migrate and differentiate.