Fig. 8.
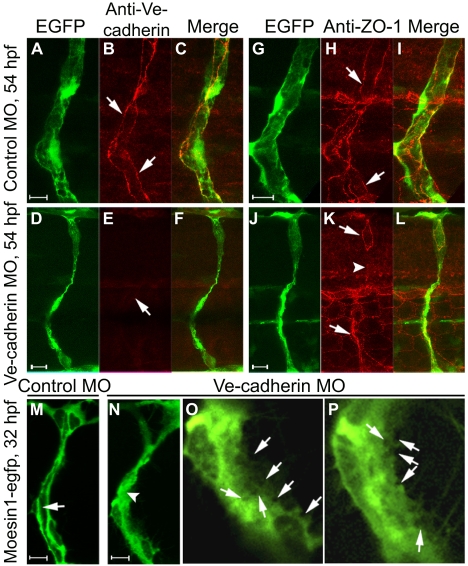
Knockdown of Ve-cadherin impairs lumen formation. (A-F) Confocal images of ISVs in Tg(fli1:egfp)y1 zebrafish embryos probed for Ve-cadherin (red) at 54 hpf. Ve-cadherin labeling (arrows) is observed in control embryos (A-C), but not in Ve-cadherin knockdown embryos (D-F). (G-L) Confocal images of ISVs in Tg(fli1:egfp)y1 embryos labeled with ZO-1 antibody (red) at 54 hpf. ZO-1-associated junctions (arrows) are observed in control embryos (G-I), but are not detected in some regions of the ISV (arrowhead) in a Ve-cadherin knockdown embryo (J-L). (M-P) Confocal images of ISVs in Tg(flk1:moesin1-egfp) embryos at 32 hpf. The primary lumen (arrow) is forming in a control embryo (M). Putative vacuoles or intercellular spaces (arrows in the higher magnification images O and P) are observed throughout the cytoplasm in endothelial cells in Ve-cadherin knockdown embryos (N-P), without formation of primary lumen (N, arrowhead).