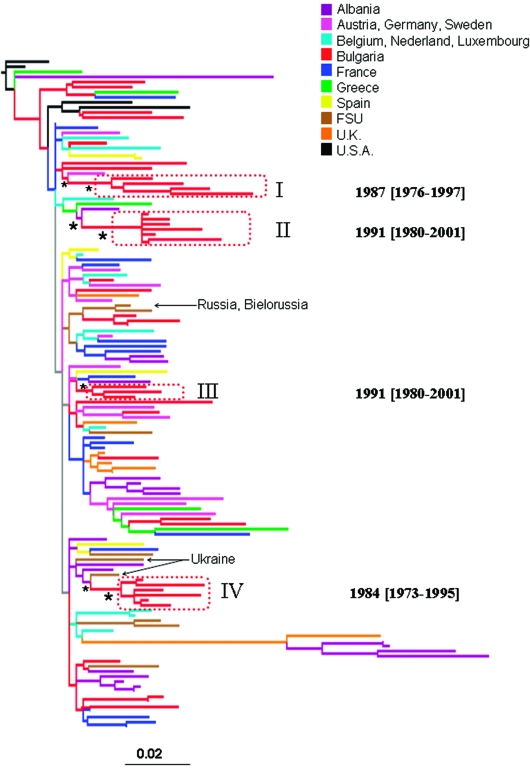
FIG. 1.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1B pol sequences. The data set included 41 HIV-1B strains from Bulgaria and 91 subtype B reference sequences downloaded from the Los Alamos HIV database. The tree was rooted by using two HIV-1A strains as the outgroup. Branch lengths were estimated with the best fitting nucleotide substitution model according to a hierarchical likelihood ratio test,11 and were drawn in scale with the bar at the bottom indicating 0.02 nucleotide substitutions per site. One asterisk (*) along a branch represents significant statistical support for the clade subtending that branch (p < 0.001 in the zero-branch-length test, Bayesian posterior probability >90%, and bootstrap support >75%). The color of each external branch represents the country of origin of the sequence corresponding to that branch, according to the legend in the figure. FSU (Former Soviet Union) strains include sequences from Russia, Bielorussia, Ukraine, and Slovenia (the specific country of origin is indicated by the arrows). Broken boxes highlight statistically supported monophyletic clades including Bulgarian strains. The inferred time of the most recent common ancestor of each supported Bulgarian clade is also indicated on the right of the highlighted clade. Dates and 95% high posterior density interval (within square brackets) were estimated using a Bayesian relaxed molecular clock (see Materials and Methods).