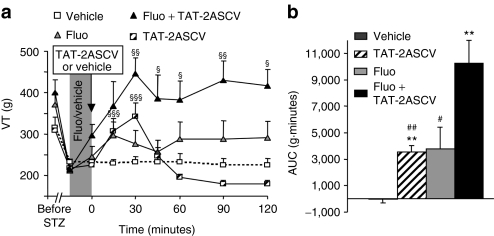
Figure 4.
Disruption of 5-HT2A receptor/PDZ protein interactions enhances SSRI-induced antihyperalgesia. (a) Diabetic hyperalgesic rats (six rats/group) received five injections (performed at 12-hour intervals) of either fluoxetine (Fluo, 10 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle (hydroxy-propyl-methyl-cellulose, HPMC, 5 ml/kg, i.p.). They were then injected intrathecally with either NaCl (10 µl/rat, vehicle) or the TAT-2ASCV peptide (30 ng/rat). §P < 0.05, §§P < 0.01, §§§P < 0.001 compared with values measured before the fluoxetine/vehicle treatment. (b) Area under the time-course (0–60 minute) curve (AUC) of vocalization threshold variations. **P < 0.01 versus vehicle; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus Fluo + TAT-2ASCV. HPMC, hydroxy-propyl-methyl-cellulose; i.p., intraperitoneal; SSRI, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; STZ, streptozocin; VT, vocalization thresholds.