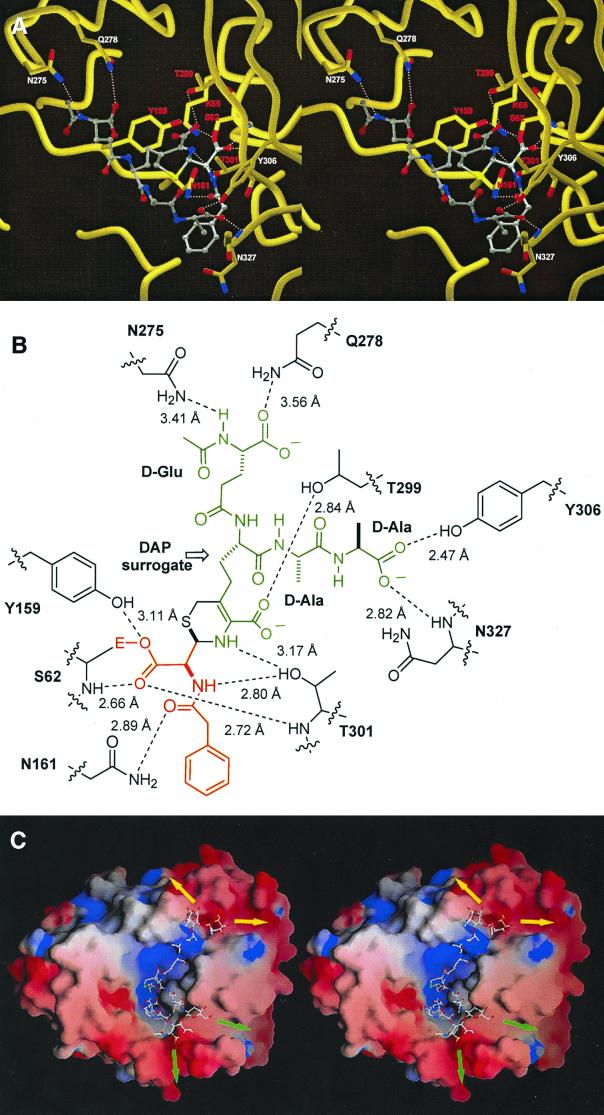
Figure 2.
(A) Stereoview of the active site of Streptomyces R61 DD-carboxypeptidase/transpeptidase acylated by cephalosporin 1, generated by using molscript (22) and RASTER3D (23, 24). The ligand is rendered as ball and stick with CPK atom colors. Hydrogen bonds between the enzyme and the ligand are shown as dotted white lines. Residues labeled in red are conserved among PBPs and β-lactamases. (B) A schematic of interactions shown in A; the red and green segments correspond with those of the same colors for species 2 shown in Fig. 1B. (C) Energy-minimized computational model of peptidoglycan strands bound to Streptomyces R61 PBP extended from the x-ray structure of species 2. The orientation of the enzyme is the same as in A. The electrostatic enzyme surface was computed in grasp (25) with blue representing positive surface charge and red representing negative surface charge. The peptidoglycan model is shown in the ball-and-stick representation, color-coded according to the atom type (N, blue; C, white; O, red; S, yellow). The positions of polymer extensions of the N-acetylglucosamine–NAM chains are shown by green arrows for the first strand and by yellow arrows for the second strand.