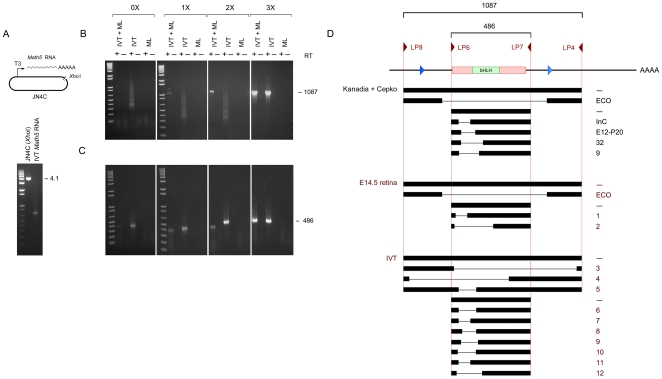
Figure 4. RT-PCRs of Math5 RNA transcribed in vitro.
A. Diagram and agarose gel showing linearized pJN4C and Math5 sense RNA generated by T3 polymerase and treated with DNaseI. B. cDNA products amplified by RT-PCR from IVT-derived RNA with UTR primers LP8 and LP4. Only the full-length 1087 bp Math5 cDNA product was amplified in the presence of 3X Masteramp (MA, indicated above brackets). In the absence of betaine, a variety of weak products were observed, with a heterogeneous deletion profile, reflecting a low level of RT template-switching. This background could be increased by using suboptimal PCR conditions or omitting the mouse liver RNA carrier. IVT, in vitro transcribed Math5 RNA (10 ng); ML, mouse liver RNA (3 µg). C. Similar RT-PCRs performed using internal primers LP6 and LP7. Only the expected 486 bp cDNA was amplified in 3X MA, while spurious products were amplified at lower MA concentrations. The right three panels in B and C represent adjacent lanes in the same gels, displayed separately for clarity. D. Alignment of lacunar cDNAs generated from IVT or E14.5 eye RNA templates. The deletion profile is comparable to the distribution reported by Kanadia and Cepko [18] (cf. Table S1 and Figure 1), using the same primer pairs with no precautions for GC secondary structure. The sequence of breakpoints is given in Table S3, with microhomology at the inferred sites of RT template-switching.