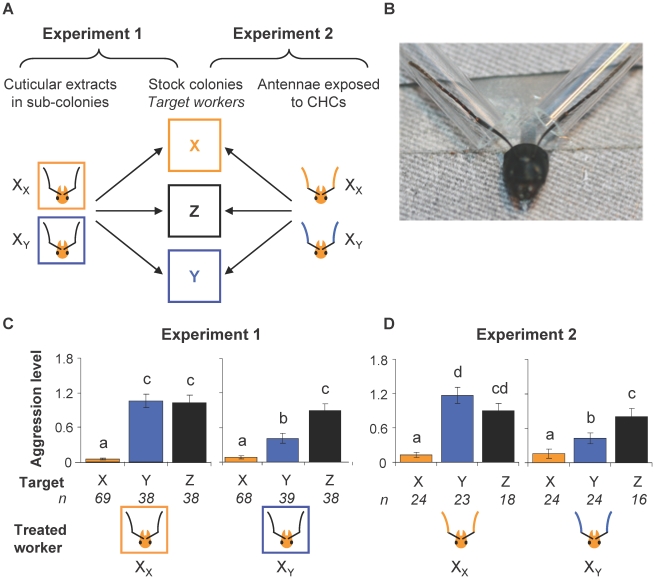
Figure 1. Effect of exposure to alien colony odor on nestmate recognition.
(A) Experimental design. Workers from colony X were exposed to the odor of either nestmates (XX) or non-nestmates from colony Y (XY), either inside sub-colonies during 24 hours (experiment 1) or directly on their antennae during 18 hours (experiment 2). Aggression tests between treated workers and anaesthetized target workers from colonies X, Y or unrelated alien Z were performed immediately after exposure as indicated by the arrows. (B) Restrained worker in the antennal exposure device. The picture shows CHC-coated glass capillaries positioned around the worker's antennae. (C, D) Aggression level of treated workers towards targets from colonies X (yellow bars), Y (blue bars) and Z (black bars) in experiments 1 (C) and 2 (D). Columns and error bars indicate mean and standard error of aggression indices respectively. Different letters indicate significant differences between categories (mixed-effects model with least square means post-hoc comparisons, P<0.05). XY workers were significantly less aggressive towards non-nestmates from colony Y than XX workers (XY–Y vs. XX–Y: P<0.0001 in both experiments). However, treatments did not influence aggressiveness towards nestmates (XX–X vs. XY–X, experiment 1: P = 0.808; experiment 2: P = 0.837) or non-nestmates from colony Z (XX–Z vs. XY–Z, experiment 1: P = 0. 322; experiment 2: P = 0. 416).