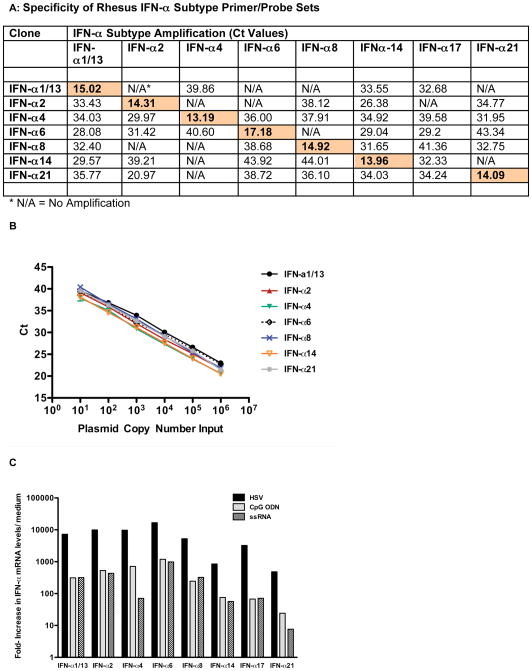
Figure 3.
Specificity and amplification of rhesus macaque IFN-α subtype primer/probe sets. Panel A: Specificity of the rhesus macaque IFN-α subtype primer/probe sets tested by PCR using IFN–α subtype-specific cDNA clones. Shown are Ct values for amplification of each distinct rhesus IFN-α subtype cDNA clone by each of the various IFN-α subtype primer/probe sets. Shaded boxes indicate IFN-α subtype specific amplification of the relevant IFN-α subtype cDNA clone. Panel B: PCR efficiency of rhesus IFN-α subtype amplification. Shown are the Ct values per input copy number for each of the IFN-α subtype cDNA clones. Amplification was linear for all rhesus IFN-α subtypes over the tested range from 10 to 10^6 copies. Panel C: IFN-α subtype induction in rhesus PBMC. Rhesus PBMC were stimulated with HSV, CpG ODN or ssRNA for 6 hours and then mRNA levels for various rhesus IFN-α subtypes were determined by real time PCR. Shown are the relative increases for each IFN-α subtype mRNA in comparison to the mRNA level of the same IFN-α subtype in medium control cultures. One representative example out of 3 experiments is shown.