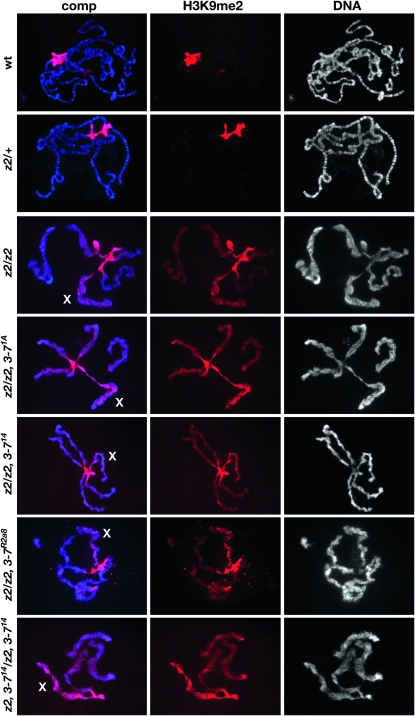
Figure 2.—
Localization of H3K9me2 in polytene chromosomes from JIL-1 and Su(var)3-7 mutant female third instar larvae. The polytene squash preparations were labeled with antibody to H3K9me2 (in red) and with Hoechst (DNA, in blue/gray). The X chromosome is indicated by an X. Preparations from wild-type (wt), heterozygous JIL-1z2/+ (z2/+), homozygous JIL-1z2/JIL-1z2 (z2/z2), JIL-1z2 Su(var)3-77.1A/JIL-1z2 (z2, 3-77.1A/z2), JIL-1z2 Su(var)3-714/JIL-1z2 (z2, 3-714/z2), JIL-1z2 Su(var)3-7R2a8/JIL-1z2 (z2, 3-7R2a8/z2), and JIL-1z2 Su(var)3-714/JIL-1z2 Su(var)3-714 (z2, 3-714/z2, 3-714) larvae are shown. In wild-type and JIL-1z2/+ preparations, H3K9me2 labeling was mainly localized to and abundant at the chromocenter; however, in the absence of the JIL-1 kinase, the H3K9me2 labeling spread to the autosomes and particularly to the X chromosome (see also Zhang et al. 2006; Deng et al. 2007). In JIL-1z2 Su(var)3-77.1A/JIL-1z2, JIL-1z2 Su(var)3-714/JIL-1z2, and JIL-1z2 Su(var)3-714/JIL-1z2 Su(var)3-714 double mutant larvae, the H3K9me2 labeling was indistiguishable from that of JIL-1z2/JIL-1z2 homozygous null mutants.