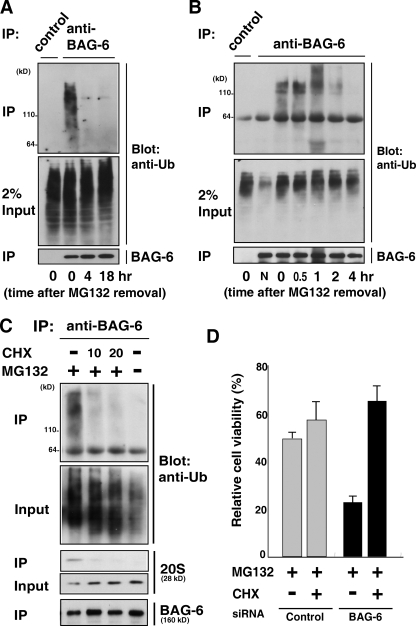
Figure 3.
BAG-6 associates with polyubiquitinated newly synthesized defective proteins. (A and B) Polyubiquitinated proteins associated with BAG-6 were degraded in vivo. HeLa cells were treated with MG132 (5 µM) for 4.5 h, the inhibitor was then washed out (this time point being defined as time zero), and the cells were cultured in a fresh medium (without MG132) for the indicated times. After harvesting the cells, endogenous BAG-6 was immunoprecipitated and the coprecipitated materials were probed with an antibody against ubiquitin. Normal rabbit immunoglobulin was used as a negative control for the immunoprecipitation procedures. “N” indicates no addition of MG132 to the cell culture. (C) Polyubiquitinated proteins associated with BAG-6 were abolished by addition of the translation inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX). HeLa cells were treated with 5 µM MG132 with or without 10 µg/ml or 20 µg/ml CHX as indicated for 1 h and then subjected to immunoprecipitation using antibody against BAG-6. The immunoprecipitates were probed with antibodies against ubiquitin, 20S proteasome, and BAG-6. (D) Depletion of BAG-6 made HeLa cells more sensitive to proteasome inhibitor-induced cell death, but the effect of BAG-6 knockdown was abrogated by adding CHX. 48 h after treatment with siRNA, cells were treated with 5 µM MG132 for 24 h with or without 10 µg/ml CHX, and cell viability was analyzed using an MTT cell counting system. The percent viability was normalized to the cells transfected with control siRNA without MG132 treatment (arbitrarily assigned a value of 100%). Error bars represent SD calculated from three experiments. P < 0.01, by t test.