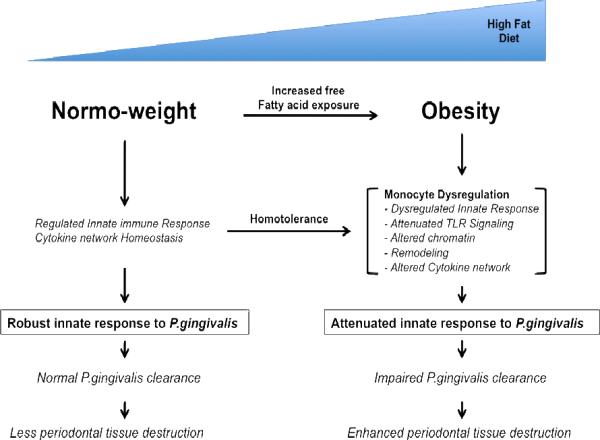
Fig. 1.
Model for proposed effect of obesity on innate response to P. gingivalis
As exposure to free-fatty acids increases, common in obese individuals, this induces homotolerance along the Toll-like receptor-2 pathway in the innate immune system. Homotolerance alters Toll-like receptor signaling pathway by altering the expression levels of Toll-like receptor-2 and possibly chromatin remodeling at the Toll-like receptor-2 gene or other gene loci involved in the signaling pathway or cytokine release. The effect of the homotolerance leads to a dysregulated innate immune response and altered cytokine network upon exposure to P.gingivalis. As a result, the innate immune system has impaired clearance of P.gingivalis, which leads to enhancement of periodontal tissue destruction